
Tonga
Veröffentlicht: 20. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
104,889
Growth: -0.34% (2024 est.)
GDP
$518.18 million
(2022 est.)
Area
747 sq km
| Government type: | constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Nuku'alofa |
| Languages: | Tongan only 85%, Tongan and other language 13.9%, Tongan not used at home 1.1% (2021 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2021 est.)
Religion (2021 est.)
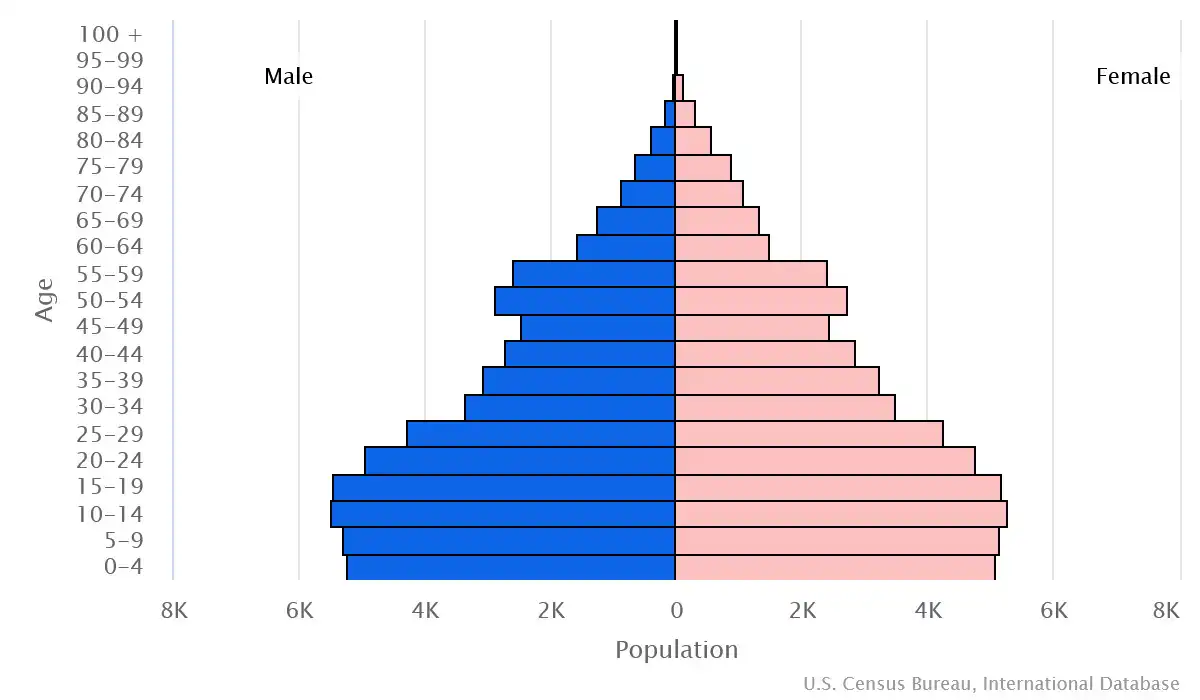
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
upper middle-income Pacific island economy; enormous diaspora and remittance reliance; key tourism and agricultural sectors; major fish exporter; rapidly growing Chinese infrastructure investments; rising methamphetamine hub
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in million $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (83%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- plastic products ♻️
- poultry 🍗
- sheep and goat meat 🥩
- cars 🚗
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (83%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- fish 🐟
- scrap copper 🟧🪙
- processed crustaceans 🦞
- vegetables 🥦
- perfume plants 🌸
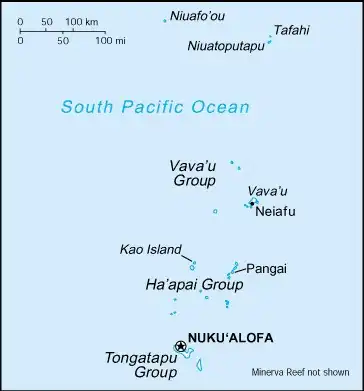
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- arable land 🌱
- fish 🐟
Climate
tropical; modified by trade winds; warm season (December to May), cool season (May to December)
Historical Background Information
The first humans arrived in Tonga around 1000 B.C. The islands’ politics were highly centralized under the Tu’i Tonga, or Tongan king, by A.D. 950, and by 1200, the Tu’i Tonga had expanded his influence throughout Polynesia and into Melanesia and Micronesia. The Tongan Empire began to decline in the 1300s, with civil wars, a military defeat to Samoa, and internal political strife. By the mid-1500s, some Tu’i Tongans were ethnic Samoan, and day-to-day administration of Tonga was transferred to a new position occupied by ethnic Tongans.
Dutch navigators explored the islands in the 1600s, followed by the British in the 1770s, who named them the Friendly Islands. Between 1799 and 1852 Tonga went through a period of war and disorder. In the 1830s, a low-ranking chief from Ha’apai began to consolidate control over the islands and was crowned King George TUPOU I in 1845, establishing the only still-extant Polynesian monarchy. During TUPOU's reign (1845–93), Tonga became a unified and independent country with a modern constitution (1875), legal code, and administrative structure. In separate treaties, Germany (1876), Great Britain (1879), and the US (1888) recognized Tonga’s independence. His son and successor, King George TUPOU II, agreed to enter a protectorate agreement with the UK in 1900 after rival Tongan chiefs tried to overthrow him. As a protectorate, Tonga never completely lost its indigenous governance, but it did become more isolated and the social hierarchy became more stratified between a group of nobles and a large class of commoners. Today, about one third of parliamentary seats are reserved for nobles.
Tonga regained full control of domestic and foreign affairs and became a fully independent nation within the Commonwealth in 1970. A pro-democracy movement gained steam in the early 2000s, led by ‘Akilisi POHIVA, and in 2006, riots broke out in Nuku’alofa to protest the lack of progress on reform. To appease the activists, in 2008, King George TUPOU V announced he was relinquishing most of his powers leading up to parliamentary elections in 2010 and henceforth most of the monarch’s governmental decisions, except those relating to the judiciary, were to be made in consultation with the prime minister. The 2010 Legislative Assembly was called Tonga’s first democratically elected Parliament. King George TUPOU V died in 2012 and was succeeded by his brother Crown Prince Tupouto‘a Lavaka who ruled as George TUPOU VI. In 2015, ‘Akalisi POHIVA became Tonga’s first non-noble prime minister.
Dutch navigators explored the islands in the 1600s, followed by the British in the 1770s, who named them the Friendly Islands. Between 1799 and 1852 Tonga went through a period of war and disorder. In the 1830s, a low-ranking chief from Ha’apai began to consolidate control over the islands and was crowned King George TUPOU I in 1845, establishing the only still-extant Polynesian monarchy. During TUPOU's reign (1845–93), Tonga became a unified and independent country with a modern constitution (1875), legal code, and administrative structure. In separate treaties, Germany (1876), Great Britain (1879), and the US (1888) recognized Tonga’s independence. His son and successor, King George TUPOU II, agreed to enter a protectorate agreement with the UK in 1900 after rival Tongan chiefs tried to overthrow him. As a protectorate, Tonga never completely lost its indigenous governance, but it did become more isolated and the social hierarchy became more stratified between a group of nobles and a large class of commoners. Today, about one third of parliamentary seats are reserved for nobles.
Tonga regained full control of domestic and foreign affairs and became a fully independent nation within the Commonwealth in 1970. A pro-democracy movement gained steam in the early 2000s, led by ‘Akilisi POHIVA, and in 2006, riots broke out in Nuku’alofa to protest the lack of progress on reform. To appease the activists, in 2008, King George TUPOU V announced he was relinquishing most of his powers leading up to parliamentary elections in 2010 and henceforth most of the monarch’s governmental decisions, except those relating to the judiciary, were to be made in consultation with the prime minister. The 2010 Legislative Assembly was called Tonga’s first democratically elected Parliament. King George TUPOU V died in 2012 and was succeeded by his brother Crown Prince Tupouto‘a Lavaka who ruled as George TUPOU VI. In 2015, ‘Akalisi POHIVA became Tonga’s first non-noble prime minister.
