
Sweden
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Stockholm |
| Languages: | Swedish (official) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2022 est.)
Religion (2021 est.)
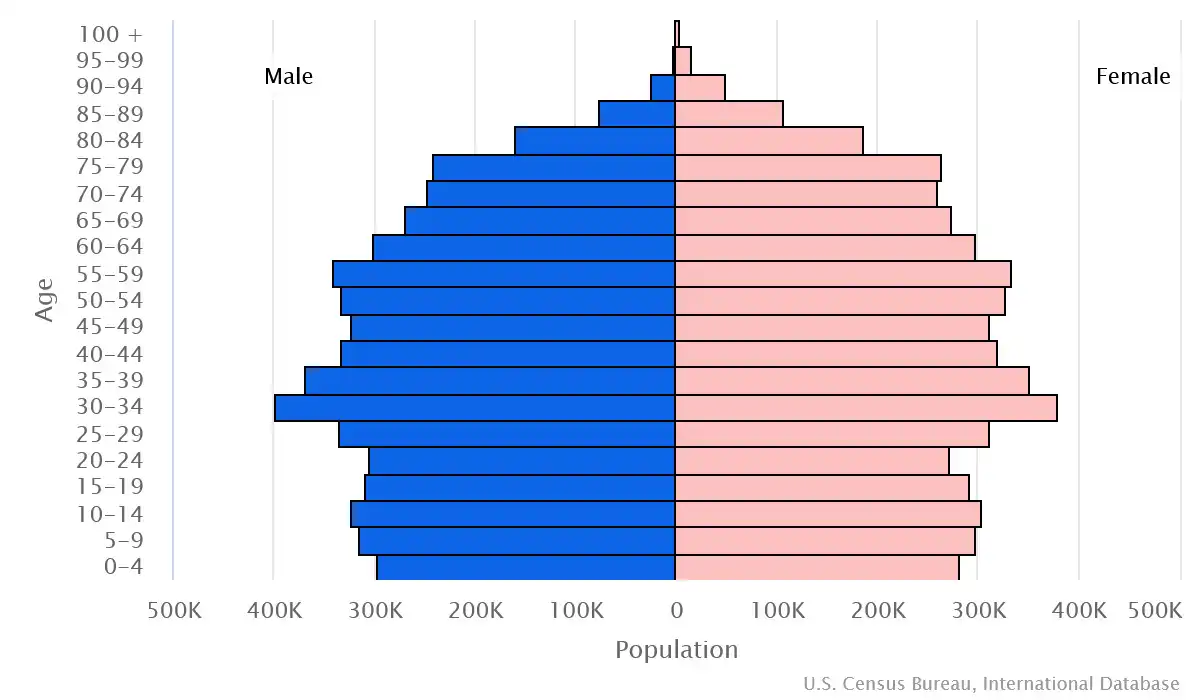
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income, largest Nordic economy; EU member but non-euro user; export-oriented led by automotive, electronics, machinery and pharmaceuticals; highly ranked for competitiveness, R&D investments and governance; slowdown triggered by high inflation, weak consumption and financial tightening
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (48%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- cars 🚗
- refined petroleum ⛽
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (48%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- packaged medicine 💊
- paper 📄
- electricity ⚡
Geography
Map
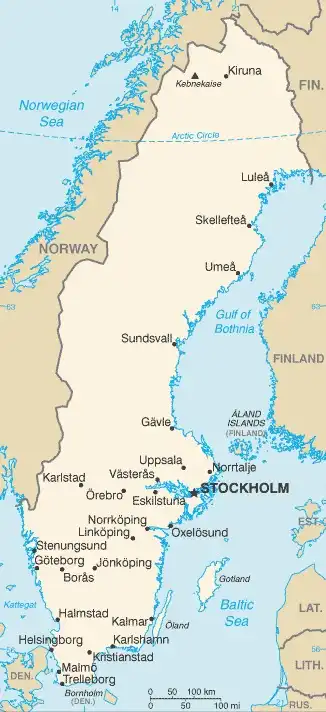
Area
Natural resources
- iron ore ⛓️
- copper 🟧🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
- tungsten 🔧
- uranium ☢️
- arsenic ☠️
- feldspar 🪨
- timber 🌲
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate
temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers; subarctic in north
Historical Background Information
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden maintained a policy of military non-alignment until it applied to join NATO in 2022. Sweden has not participated in any war for two centuries. Stockholm preserved an armed neutrality in both World Wars. Since then, Sweden has pursued a successful economic formula consisting of a capitalist system intermixed with substantial welfare elements. Sweden joined the EU in 1995, but the public rejected the introduction of the euro in a 2003 referendum. The share of Sweden’s population born abroad increased from 11.3% in 2000 to 20% in 2022.
