
Slovakia
Veröffentlicht: 20. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
5,563,649
Growth: -0.08% (2024 est.)
GDP
$132.908 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
49,035 sq km
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
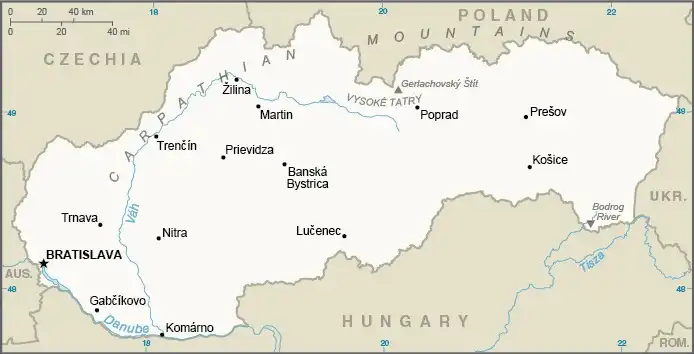
| Capital: | Bratislava |
| Languages: | Slovak (official) 81.8%, Hungarian 8.5%, Roma 1.8%, other 2.2%, unspecified 5.7% (2021 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2021 est.)
Religion (2021 est.)
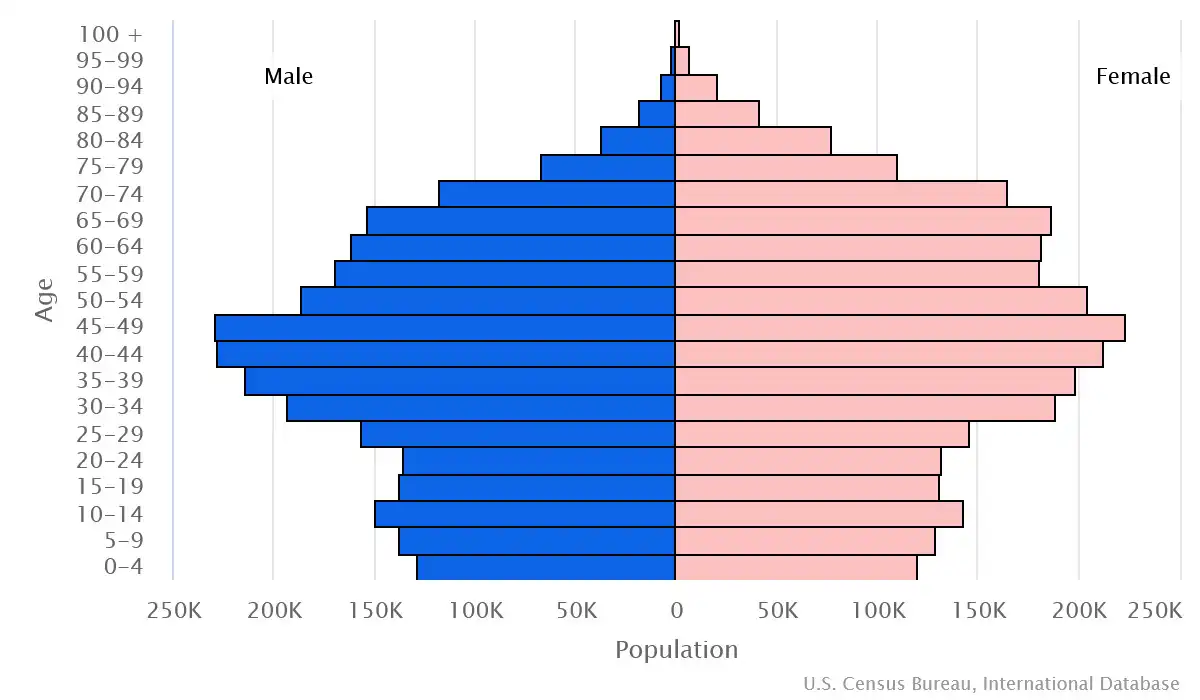
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income EU- and eurozone-member economy; manufacturing and exports led by automotive sector; weakening of anti-corruption laws may impact foreign investment and status of EU funds; influx of foreign labor offsets aging workforce; widening fiscal deficit from social spending and EU-financed public investments
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (56%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- natural gas 💨
- cars 🚗
- electricity ⚡
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (56%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- cars 🚗
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- video displays 📺
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- electricity ⚡
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- lignite 🪨
- small amounts of iron ore ⛓️
- copper and manganese ore 🟧🪙
- salt 🧂
- arable land 🌱
Climate
temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
Historical Background Information
Slovakia traces its roots to the 9th century state of Great Moravia. The Slovaks then became part of the Hungarian Kingdom, where they remained for the next 1,000 years. After the formation of the dual Austro-Hungarian monarchy in 1867, language and education policies favoring the use of Hungarian (known as "Magyarization") led to a public backlash that boosted Slovak nationalism and strengthened Slovak cultural ties with the closely related Czechs, who fell administratively under the Austrian half of the empire. When the Austro-Hungarian Empire dissolved at the end of World War I, the Slovaks joined the Czechs to form Czechoslovakia. During the interwar period, Slovak nationalist leaders pushed for autonomy within Czechoslovakia, and in 1939, in the wake of Germany's annexation of the Sudetenland, the newly established Slovak Republic became a German client state for the remainder of World War II.
After World War II, Czechoslovakia was reconstituted and came under communist rule within Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe. In 1968, Warsaw Pact troops invaded and ended the efforts of Czechoslovakia's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful Velvet Revolution swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Slovakia joined both NATO and the EU in 2004 and the euro zone in 2009.
After World War II, Czechoslovakia was reconstituted and came under communist rule within Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe. In 1968, Warsaw Pact troops invaded and ended the efforts of Czechoslovakia's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful Velvet Revolution swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Slovakia joined both NATO and the EU in 2004 and the euro zone in 2009.
