
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Veröffentlicht: 20. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
100,647
Growth: -0.15% (2024 est.)
GDP
$1.066 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
389 sq km
Saint Vincent 344 sq km
| Government type: | parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm |
| Capital: | Kingstown |
| Languages: | English, Vincentian Creole English, French patois |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2012 est.)
Religion (2012 est.)
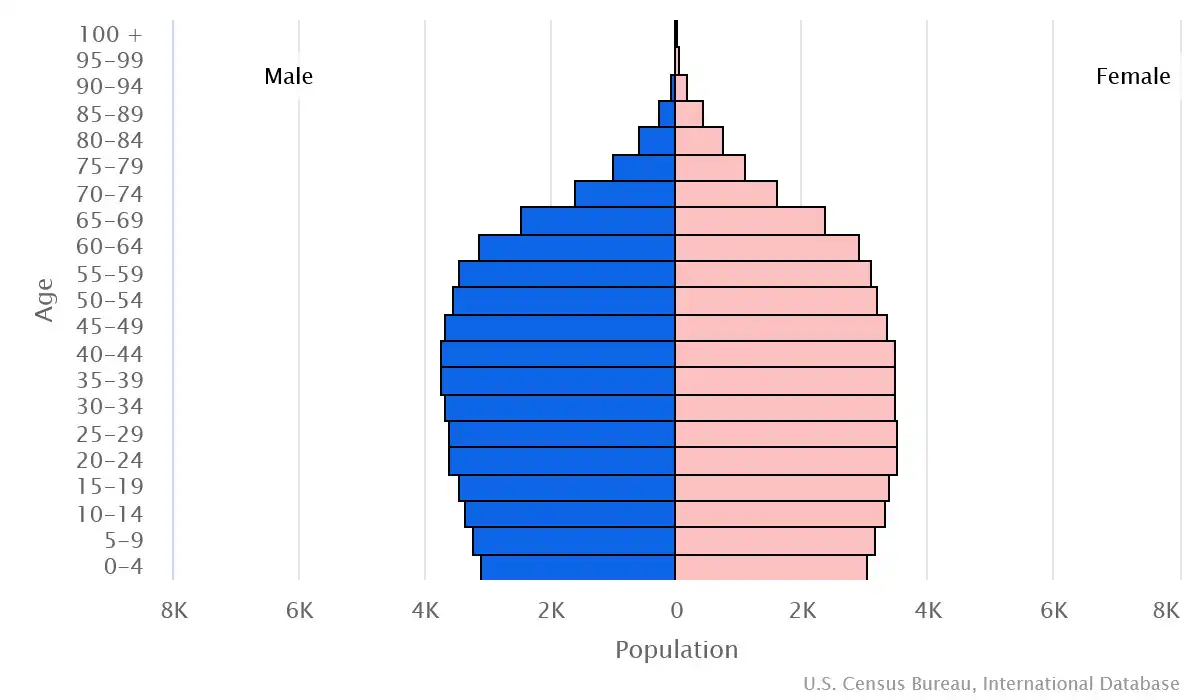
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
upper middle-income Caribbean island economy; key agriculture and tourism sectors; environmentally fragile; diversifying economy across services, science and knowledge, and creative industries; CARICOM member and US Caribbean Basin Initiative beneficiary
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in million $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (67%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- poultry 🍗
- ships 🚢
- raw sugar 🍚
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (67%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- ships 🚢
- fish 🐟
- shellfish 🐟
- wheat 🌾
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- hydropower 💧⚡
- arable land 🌱
Climate
tropical; little seasonal temperature variation; rainy season (May to November)
Historical Background Information
Resistance from native Caribs prevented colonization on Saint Vincent until 1719. France and England disputed the island for most of the 18th century, but it was ceded to England in 1783. The British prized Saint Vincent because of its fertile soil, which allowed for thriving slave-run plantations of sugar, coffee, indigo, tobacco, cotton, and cocoa. In 1834, the British abolished slavery. Immigration of indentured servants eased the ensuing labor shortage, as did subsequent immigrant waves from Portugal and East India. Conditions remained harsh for both former slaves and immigrant agricultural workers, however, as depressed world sugar prices kept the economy stagnant until the early 1900s. The economy then went into a period of decline, with many landowners abandoning their estates and leaving the land to be cultivated by liberated slaves.
Between 1960 and 1962, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a separate administrative unit of the Federation of the West Indies. Autonomy was granted in 1969 and independence in 1979. In 2021, the eruption of the La Soufrière volcano in the north of Saint Vincent destroyed much of Saint Vincent’s most productive agricultural lands. Unlike most of its tourism-dependent neighbors, the Vincentian economy is primarily agricultural.
Between 1960 and 1962, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a separate administrative unit of the Federation of the West Indies. Autonomy was granted in 1969 and independence in 1979. In 2021, the eruption of the La Soufrière volcano in the north of Saint Vincent destroyed much of Saint Vincent’s most productive agricultural lands. Unlike most of its tourism-dependent neighbors, the Vincentian economy is primarily agricultural.
