
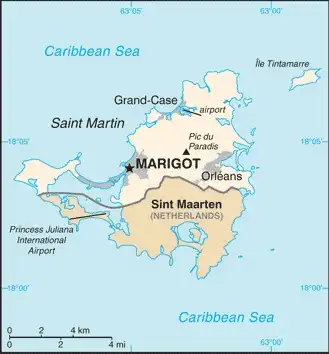
Saint Martin
Veröffentlicht: 20. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
32,996
Growth: 0.3% (2024 est.)
GDP
$649.206 million
(2021 est.)
Area
50 sq km
| Government type: | parliamentary democracy (Territorial Council); overseas collectivity of France |
| Capital: | Marigot |
| Languages: | French (official), Dutch, English, Guadeloupian Creole, Haitian Creole, Italian, Martiniquan Creole, Papiamento (dialect of Netherlands Antilles), Spanish |
People & Society
Ethnicity (French-East Asian)
Religion
Age structure
No image available.
Economy
Economic overview
high-income French Caribbean territorial economy; extremely reliant on tourism, with severe COVID-19 impacts; near-total destruction from Hurricane Irma in 2017; some offshore banking; import-dependent; duty-free commerce; yachting destination
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
no data
Real GDP per capita in $
No data
Top 5 Import Partner in 2019 (90%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2019
- jewelry 💍
- diamonds 💎
- pearls 🦪
- recreational boats ⛵
- cars 🚗
Top 5 Export Partner in 2019 (90%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2019
- gold 💰
- special use vessels 🚢
- furniture 🛋️
- scrap aluminum 🪙
- rum 🍹
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- salt 🧂
Climate
temperature averages 27-29 degrees Celsius all year long; low humidity, gentle trade winds, brief, intense rain showers; hurricane season stretches from July to November
Historical Background Information
Christopher COLUMBUS claimed Saint Martin for Spain in 1493, naming it after the feast day of St. Martin of Tours, but it was the Dutch who occupied the island in 1631 to exploit its salt deposits. The Spanish retook Saint Martin in 1633, but the Dutch continued to assert their claims. The Spanish finally relinquished the island to the French and Dutch, who divided it between themselves in 1648. The border frequently fluctuated over the next 200 years because of friction between the two countries, with the French eventually holding the greater portion of the island (about 61%).
The cultivation of sugarcane introduced African slavery to the island in the late 18th century; the practice was not abolished until 1848. The island became a free port in 1939, and the tourism industry was dramatically expanded during the 1970s and 1980s. In 2003, the populace of Saint Martin voted to secede from Guadeloupe, and in 2007, the northern portion of the island became a French overseas collectivity. In 2010, the southern Dutch portion of the island became the independent nation of Sint Maarten within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 2017, Hurricane Irma passed over the island of Saint Martin, causing extensive damage to roads, communications, electrical power, and housing; the UN estimated that 90% of the buildings were damaged or destroyed.
The cultivation of sugarcane introduced African slavery to the island in the late 18th century; the practice was not abolished until 1848. The island became a free port in 1939, and the tourism industry was dramatically expanded during the 1970s and 1980s. In 2003, the populace of Saint Martin voted to secede from Guadeloupe, and in 2007, the northern portion of the island became a French overseas collectivity. In 2010, the southern Dutch portion of the island became the independent nation of Sint Maarten within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 2017, Hurricane Irma passed over the island of Saint Martin, causing extensive damage to roads, communications, electrical power, and housing; the UN estimated that 90% of the buildings were damaged or destroyed.
