
Russia
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | semi-presidential federation |
| Capital: | Moscow |
| Languages: | Russian (official) 85.7%, Tatar 3.2%, Chechen 1%, other 10.1% (2010 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2010 est.)
Religion (2006 est.)
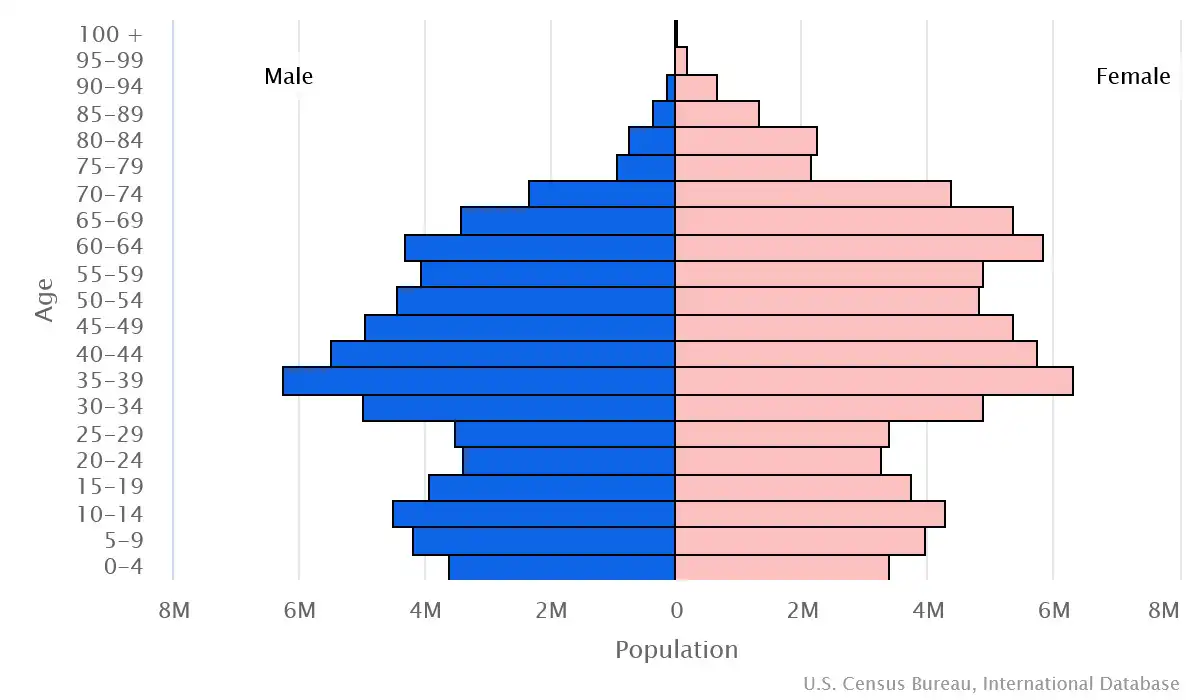
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
natural resource-rich Eurasian economy; leading energy exporter to Europe and Asia; decreased oil export reliance; endemic corruption, Ukrainian invasion, and lack of green infrastructure limit investment and have led to sanctions
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (60%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- packaged medicine 💊
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (60%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- coal ⚫
- fertilizers 💩
Geography
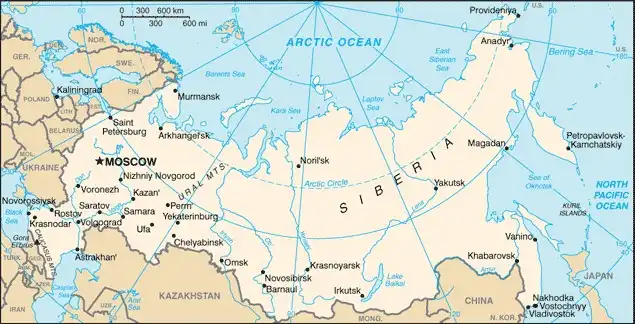
Map
Area
Natural resources
- wide natural-resource base including major deposits of oil 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- coal ⚫
- and many strategic minerals 🪙
- bauxite 🪨
- reserves of rare earth elements 🪨🪙💎
- timber 🌲
Climate
ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia; subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north; winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia; summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast
Historical Background Information
Founded in the 12th century, the Principality of Muscovy emerged from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and gradually conquered and absorbed surrounding principalities. In the early 17th century, a new ROMANOV dynasty continued this policy of expansion across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in the formation of a parliament and other reforms. Devastating defeats and food shortages in World War I led to widespread rioting in the major cities of the Russian Empire and to the overthrow of the ROMANOV Dynasty in 1917. The communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR).
The brutal rule of Iosif STALIN (1928-53) strengthened communist control and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at a cost of tens of millions of lives. After defeating Germany in World War II as part of an alliance with the US (1939-1945), the USSR expanded its territory and influence in Eastern Europe and emerged as a global power. The USSR was the principal US adversary during the Cold War (1947-1991). The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the decades following Stalin's rule, until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize communism. His initiatives inadvertently released political and economic forces that by December 1991 led to the dissolution of the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent states. In response to the ensuing turmoil during President Boris YELTSIN's term (1991-99), Russia shifted toward a centralized authoritarian state under President Vladimir PUTIN (2000-2008, 2012-present) in which the regime seeks to legitimize its rule through managed elections, populist appeals, a foreign policy focused on enhancing the country's geopolitical influence, and commodity-based economic growth.
In 2014, Russia purported to annex Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula and occupied large portions of two eastern Ukrainian oblasts. In sporadic fighting over the next eight years, more than 14,000 civilians were killed or wounded as a result of the Russian invasion in eastern Ukraine. On 24 February 2022, Russia escalated its conflict with Ukraine by invading the country on several fronts in what has become the largest conventional military attack on a sovereign state in Europe since World War II. The invasion received near-universal international condemnation, and many countries imposed sanctions on Russia and supplied humanitarian and military aid to Ukraine. In September 2022, Russia unilaterally declared its annexation of four Ukrainian oblasts -- Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporizhzhia -- even though none were fully under Russian control. The annexations remain unrecognized by the international community.
