
Nicaragua
Veröffentlicht: 19. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
6,676,948
Growth: 0.95% (2024 est.)
GDP
$17.829 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
130,370 sq km
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Managua |
| Languages: | Spanish (official) 99.5%, Indigenous 0.3%, Portuguese 0.1%, other 0.1% (2020 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (mixed Indigenous and White)
Religion (2020 est.)
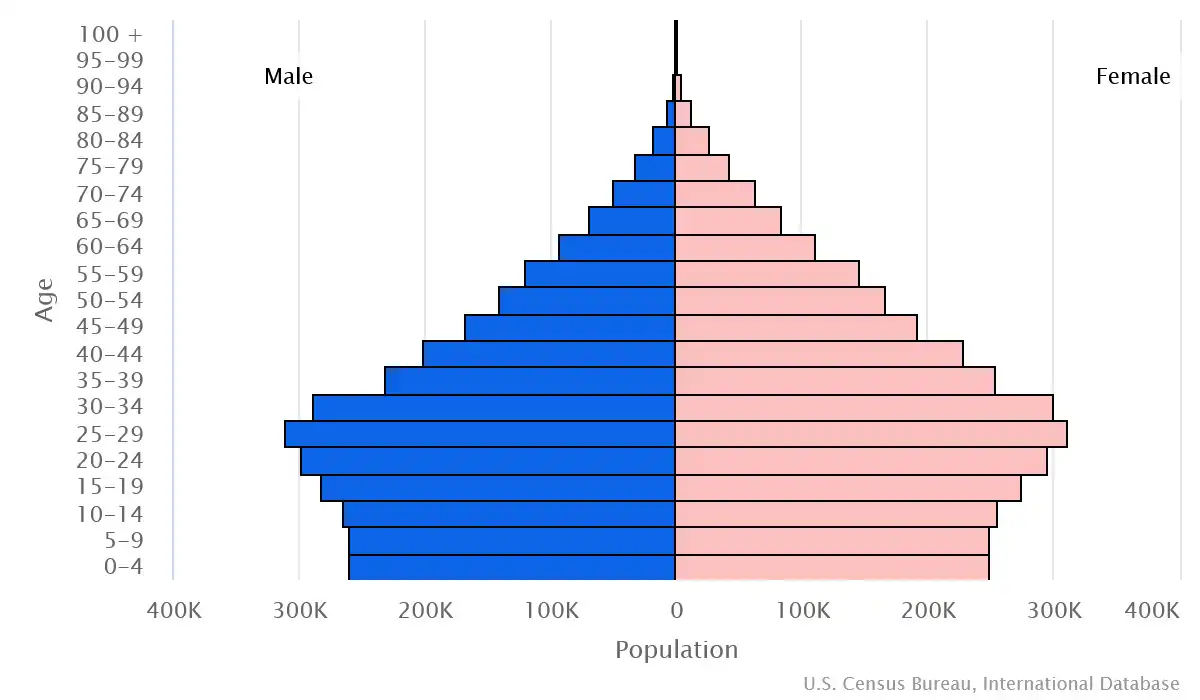
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
low-income Central American economy; until 2018, nearly 20 years of sustained GDP growth; recent struggles due to COVID-19, political instability, and hurricanes; significant remittances; increasing poverty and food scarcity since 2005; sanctions limit investment
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (65%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- garments 👕
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fabric 👕🧶
- plastic products ♻️
- crude petroleum 🛢️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (65%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- garments 👕
- gold 💰
- coffee ☕
- insulated wire 🔌
- beef 🥩
Geography
Map
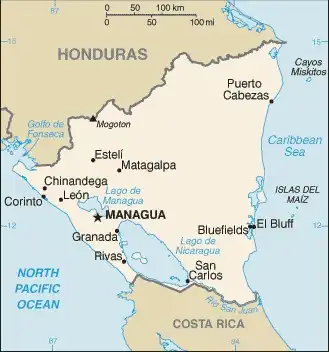
Area
Natural resources
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
- copper 🟧🪙
- tungsten 🔧
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- timber 🌲
- fish 🐟
Climate
tropical in lowlands, cooler in highlands
Historical Background Information
The Pacific coast of Nicaragua was settled as a Spanish colony in the early 16th century. Independence from Spain was declared in 1821, and the country became an independent republic in 1838. Britain occupied the Caribbean Coast in the first half of the 19th century, but gradually ceded control of the region in subsequent decades. By 1978, violent opposition to governmental manipulation and corruption resulted in a short-lived civil war that brought a civil-military coalition to power in 1979, spearheaded by Marxist Sandinista guerrillas led by Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra. Nicaraguan aid to leftist rebels in El Salvador prompted the US to sponsor anti-Sandinista Contra guerrillas through much of the 1980s.
After losing free and fair elections in 1990, 1996, and 2001, ORTEGA was elected president in 2006, 2011, 2016, and most recently in 2021. Municipal, regional, and national-level elections since 2008 have been marred by widespread irregularities. Democratic institutions have lost their independence under the ORTEGA regime as the president has assumed full control over all branches of government, as well as cracking down on a nationwide pro-democracy protest movement in 2018 and shuttering over 3,300 civil society organizations between 2018 and 2024. In the lead-up to the 2021 presidential election, authorities arrested over 40 individuals linked to the opposition, including presidential candidates, private sector leaders, NGO workers, human rights defenders, and journalists. Only five lesser-known presidential candidates from mostly small parties allied to ORTEGA's Sandinistas were allowed to run against ORTEGA. He then awarded the Sandinistas control of all 153 of Nicaraguan municipalities in the 2022 municipal elections, consolidating one-party rule.
After losing free and fair elections in 1990, 1996, and 2001, ORTEGA was elected president in 2006, 2011, 2016, and most recently in 2021. Municipal, regional, and national-level elections since 2008 have been marred by widespread irregularities. Democratic institutions have lost their independence under the ORTEGA regime as the president has assumed full control over all branches of government, as well as cracking down on a nationwide pro-democracy protest movement in 2018 and shuttering over 3,300 civil society organizations between 2018 and 2024. In the lead-up to the 2021 presidential election, authorities arrested over 40 individuals linked to the opposition, including presidential candidates, private sector leaders, NGO workers, human rights defenders, and journalists. Only five lesser-known presidential candidates from mostly small parties allied to ORTEGA's Sandinistas were allowed to run against ORTEGA. He then awarded the Sandinistas control of all 153 of Nicaraguan municipalities in the 2022 municipal elections, consolidating one-party rule.
