
Netherlands
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy; part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands |
| Capital: | Amsterdam; note - The Hague is the seat of government |
| Languages: | Dutch (official), Frisian (official in Fryslan province) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2021 est.)
Religion (2019 est.)
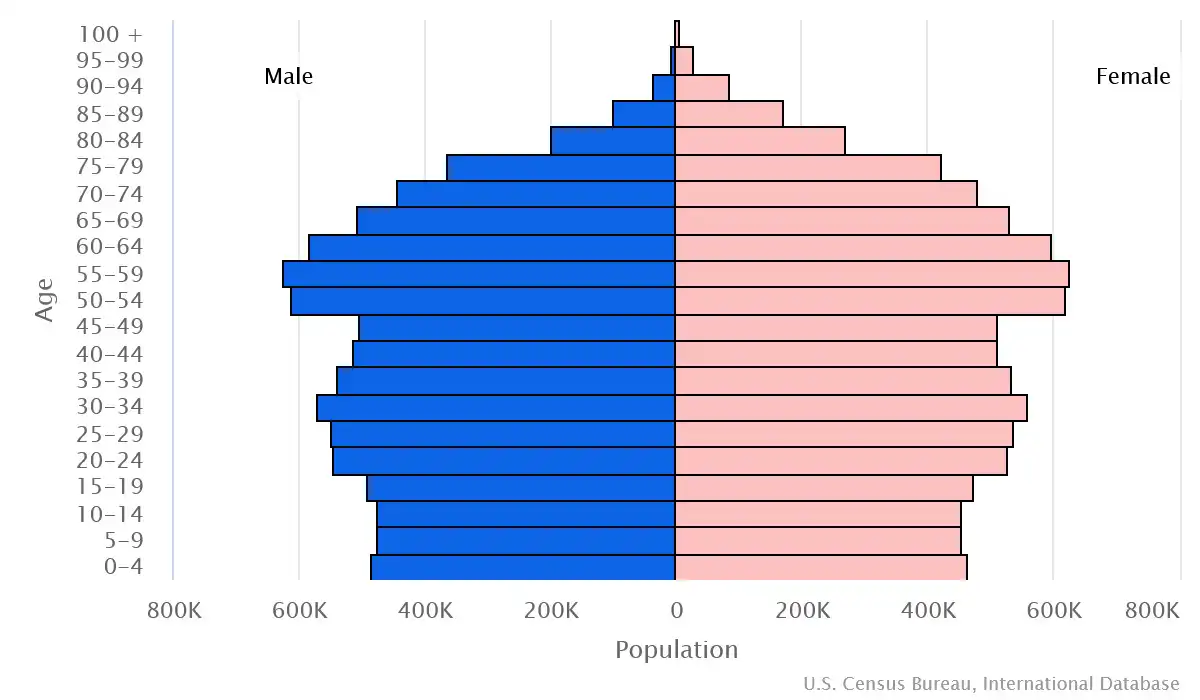
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income, core EU- and eurozone-member economy; trade-oriented with strong services, logistics, and high tech sectors; exiting mild recession triggered by inflation and weak export demand; tight labor market; low deficits and manageable public debt; strong ratings for innovation, competitiveness, and business climate
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (49%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- refined petroleum ⛽
- natural gas 💨
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- computers 💻
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (49%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- machinery ⚙️
- packaged medicine 💊
- crude petroleum 🛢️
Geography
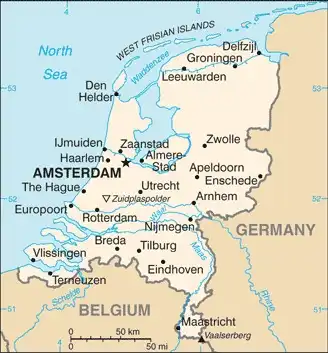
Map
Area
Natural resources
- natural gas 💨
- petroleum 🛢️
- peat 🪵
- limestone 🪨
- salt 🧂
- sand and gravel 🏜️
- arable land 🌱
Climate
temperate; marine; cool summers and mild winters
Historical Background Information
The Dutch United Provinces declared their independence from Spain in 1581; during the 17th century, they became a leading seafaring and commercial power, with settlements and colonies around the world. After 18 years of French domination, the Netherlands regained its independence in 1813. In 1830, Belgium seceded and formed a separate kingdom. The Netherlands remained neutral in World War I but suffered German invasion and occupation in World War II. A modern, industrialized nation, the Netherlands is also a large exporter of agricultural products. The country was a founding member of NATO and the EEC (now the EU) and participated in the introduction of the euro in 1999. In 2010, the former Netherlands Antilles was dissolved and the three smallest islands -- Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba -- became special municipalities in the Netherlands administrative structure. The larger islands of Sint Maarten and Curacao joined the Netherlands and Aruba as constituent countries forming the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
In 2018, the Sint Eustatius island council (governing body) was dissolved and replaced by a government commissioner to restore the integrity of public administration. According to the Dutch Government, the intervention will be as "short as possible and as long as needed."
