
Micronesia
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | federal republic in free association with the US |
| Capital: | Palikir |
| Languages: | English (official and common language), Chuukese, Kosrean, Pohnpeian, Yapese, Ulithian, Woleaian, Nukuoro, Kapingamarangi |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2010 est.)
Religion (2010 est.)
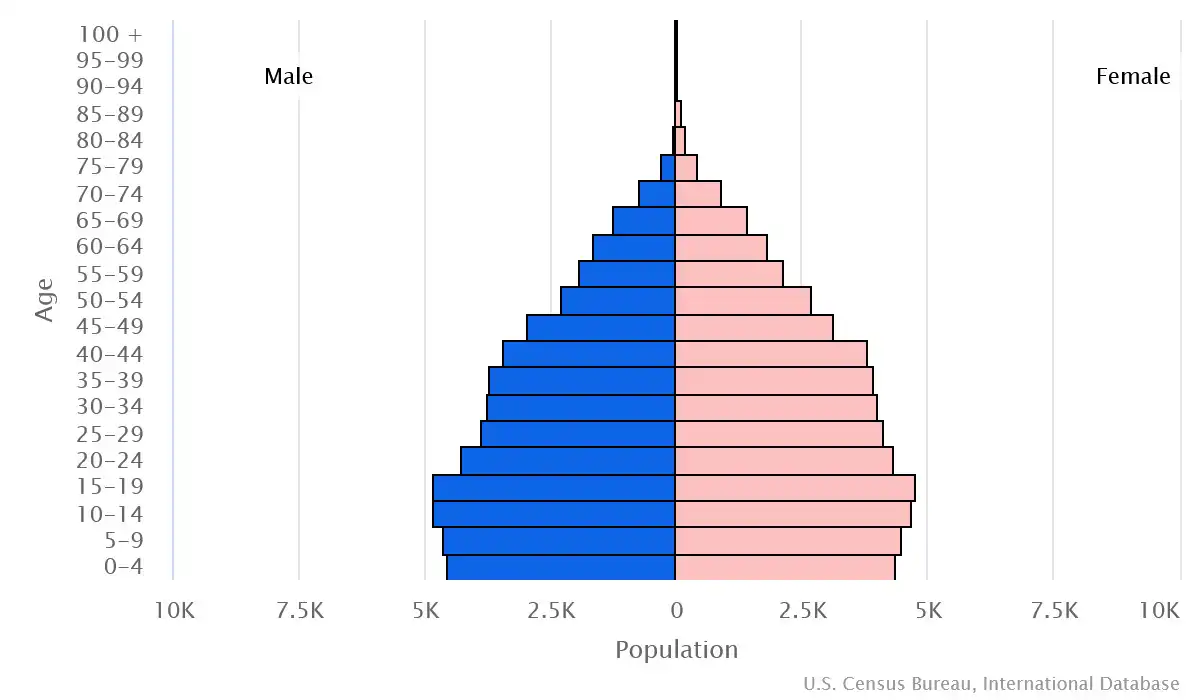
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
lower middle-income Pacific island economy; US aid reliance, sunsetting in 2024; low entrepreneurship; mostly fishing and farming; US dollar user; no patent laws; tourism remains underdeveloped; significant corruption
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in million $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (81%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- plastic products ♻️
- ships 🚢
- poultry 🍗
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fish 🐟
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (81%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- fish 🐟
- integrated circuits 💻
- garments 👕
- aircraft parts ✈️
- broadcasting equipment 📡
Geography
Map
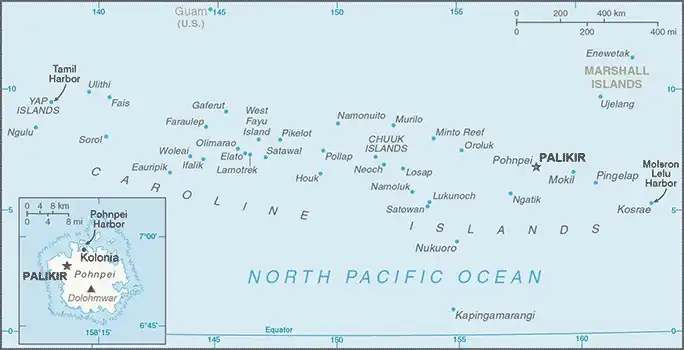
Area
Natural resources
- timber 🌲
- marine products 🐟
- deep-seabed minerals 🪨🌊
- phosphate 🧪
Climate
tropical; heavy year-round rainfall, especially in the eastern islands; located on southern edge of the typhoon belt with occasionally severe damage
Historical Background Information
Each of the four states that compose the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) -- Chuuk, Kosrae, Pohnpei, and Yap -- has its own unique history and cultural traditions. The first humans arrived in what is now the FSM in the second millennium B.C. In the 800s A.D., construction of the artificial islets at the Nan Madol complex in Pohnpei began, with the main architecture being built around 1200. At its height, Nan Madol united the approximately 25,000 people of Pohnpei under the Saudeleur Dynasty. By 1250, Kosrae was united in a kingdom centered in Leluh. Yap’s society became strictly hierarchical, with chiefs receiving tributes from islands up to 1,100 km (700 mi) away. Widespread human settlement in Chuuk began in the 1300s, and the different islands in the Chuuk Lagoon were frequently at war with one another.
Portuguese and Spanish explorers visited a few of the islands in the 1500s, and Spain began exerting nominal, but not day-to-day, control over some of the islands -- which they named the Caroline Islands -- in the 1600s. In 1899, Spain sold all of the FSM to Germany. Japan seized the islands in 1914 and was granted a League of Nations mandate to administer them in 1920. The Japanese navy built bases across most of the islands and headquartered their Pacific naval operations in Chuuk. The US bombed Chuuk in 1944 but largely bypassed the other islands in its leapfrog campaign across the Pacific.
In 1947, the FSM came under US administration as part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, which comprised six districts: Chuuk, the Marshall Islands, the Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Pohnpei, and Yap; Kosrae was separated from Pohnpei into a separate district in 1977. In 1979, Chuuk, Kosrae, Pohnpei, and Yap ratified the FSM Constitution and declared independence while the other three districts opted to pursue separate political status. There are significant inter-island rivalries stemming from their different histories and cultures. Chuuk, the most populous but poorest state, has pushed for secession, but an independence referendum has been repeatedly postponed.
