
Malawi
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Lilongwe |
| Languages: | English (official), Chewa (dominant), Lambya, Lomwe, Ngoni, Nkhonde, Nyakyusa, Nyanja, Sena, Tonga, Tumbuka, Yao |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2018 est.)
Religion (2018 est.)
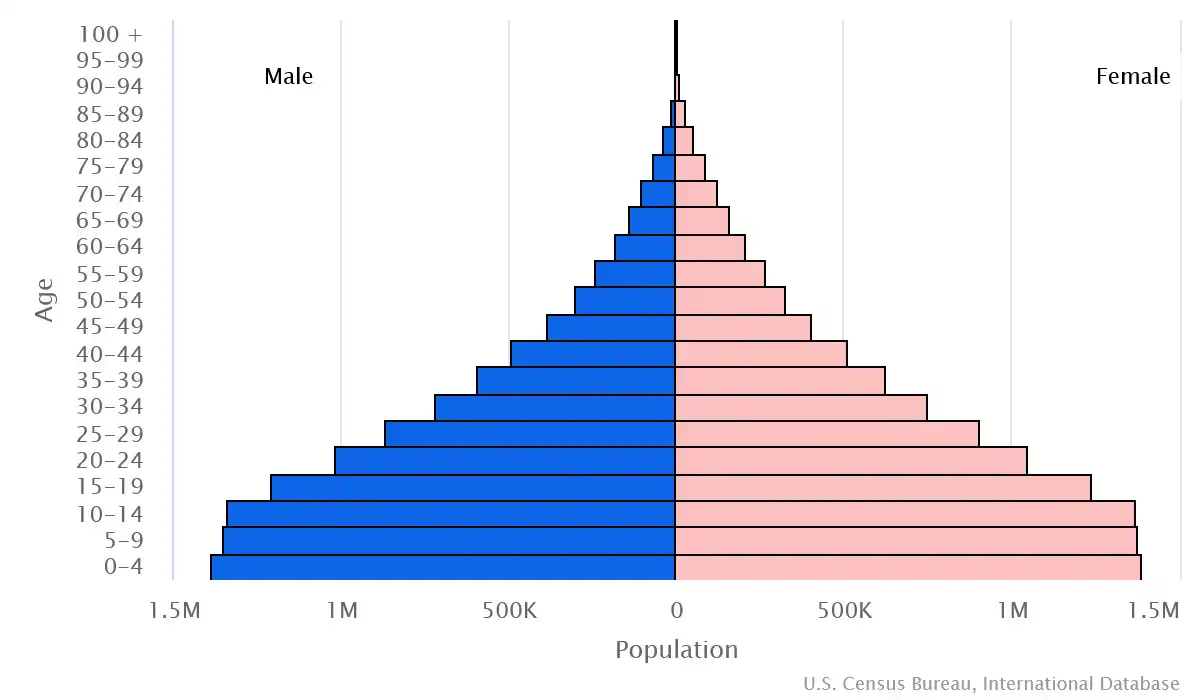
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
low-income East African economy; primarily agrarian; investing in human capital; urban poverty increasing due to COVID-19; high public debt; endemic corruption and poor property rights; poor hydroelectric grid; localized pharmaceutical industry
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (57%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fertilizers 💩
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- packaged medicine 💊
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (57%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- tobacco 🚬
- gold 💰
- tea 🍵
- ground nuts 🌰
- dried legumes 🌰
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- limestone 🪨
- arable land 🌱
- hydropower 💧⚡
- unexploited deposits of uranium ☢️
- coal ⚫
- and bauxite 🪨
Climate
sub-tropical; rainy season (November to May); dry season (May to November)
Historical Background Information
Malawi shares its name with the Chewa word for flames and is linked to the Maravi people from whom the Chewa language originated. The Maravi settled in what is now Malawi around 1400, during one of the later waves of Bantu migration across central and southern Africa. A powerful Maravi kingdom established around 1500 reached its zenith around 1700, when it controlled what is now southern and central Malawi and portions of neighboring Mozambique and Zambia. The kingdom eventually declined because of destabilization from the escalating global trade in enslaved people. In the early 1800s, widespread conflict in southern Africa displaced various ethnic Ngoni groups, some of which moved into Malawi and further undermined the Maravi. Members of the Yao ethnic group -- which had long traded with Malawi from Mozambique -- introduced Islam and began to settle in Malawi in significant numbers in the mid-1800s, followed by members of the Lomwe ethnic group. British missionary and trading activity increased in the area around Lake Nyasa in the mid-1800s, and in 1891, Britain declared a protectorate called British Central Africa over what is now Malawi. The British renamed the territory Nyasaland in 1907, and it was part of the colonial Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland -- including present-day Zambia and Zimbabwe -- from 1953 to 1963 before gaining independence as Malawi in 1964.
Hastings Kamuzu BANDA served as prime minister at independence and then as president when the country became a republic in 1966. He later instituted one-party rule under his Malawi Congress Party (MCP) and was declared president for life. After three decades of one-party rule, the country held multiparty presidential and parliamentary elections in 1994 under a provisional constitution that came into full effect the following year. Bakili MULUZI of the United Democratic Front party became the first freely elected president of Malawi when he defeated BANDA at the polls in 1994; he won reelection in 1999. President Bingu wa MUTHARIKA was elected in 2004 and reelected to a second term in 2009. He died abruptly in 2012 and was succeeded by Vice President Joyce BANDA. MUTHARIKA's brother, Peter MUTHARIKA, defeated BANDA in the election in 2014. Peter MUTHARIKA was reelected in a disputed election in 2019 that resulted in countrywide protests. The courts ordered a new election, and in 2020, Lazarus CHAKWERA of the MCP was elected president. Population growth, increasing pressure on agricultural lands, corruption, and HIV/AIDS pose major problems for Malawi.
