
Macau
Veröffentlicht: 19. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
644,426
Growth: 0.67% (2024 est.)
GDP
$45.803 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
28 sq km
| Government type: | executive-led limited democracy; a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China |
| Capital: | - |
| Languages: | Cantonese 81%, Mandarin 4.7%, other Chinese dialects 5.4%, English 3.6%, Tagalog 2.9%, Portuguese 0.6%, other 1.8% (2021 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2021 est.)
Religion (2020 est.)
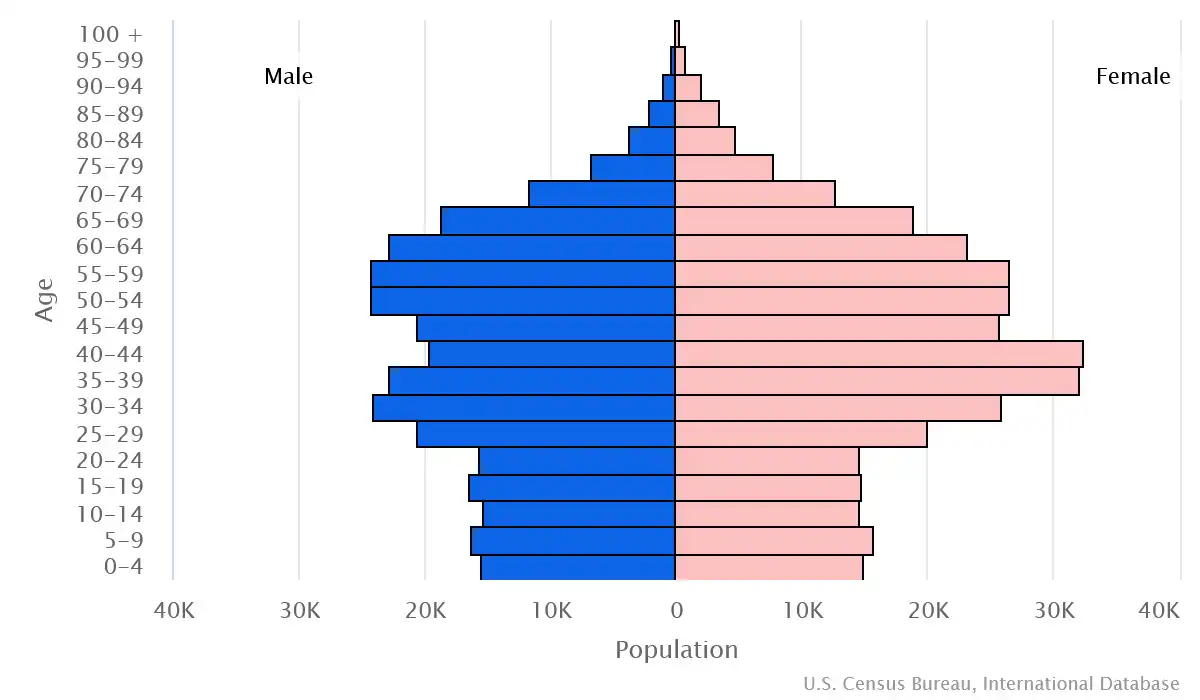
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income, Chinese special administrative region economy; known for apparel exports and gambling tourism; currency pegged to Hong Kong dollar; significant recession due to 2015 Chinese anticorruption campaign; COVID-19 further halved economic activity
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (76%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- jewelry 💍
- garments 👕
- electricity ⚡
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- trunks and cases 🧳
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (76%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- jewelry 💍
- garments 👕
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- precious metal watches ⌚
- trunks and cases 🧳
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- NEGL
Climate
subtropical; marine with cool winters, warm summers
Historical Background Information
Portuguese ships began arriving in 1513. In the 1550s, Portuguese paying tribute to China settled in Macau, which became the official entrepôt for all international trade with China and Japan and the first European settlement in the Far East. The first governor was appointed in the 17th century, but the Portuguese remained largely under the control of the Chinese. In the 1930s and ’40s Macau was declared a neutral territory during the Sino-Japanese War and World War II and became a refuge for both Chinese and Europeans. Portugal officially made Macau an overseas province in 1951.
In April 1987, Portugal and China reached an agreement to return Macau to Chinese rule in 1999, using the Hong Kong Joint Declaration between China and the UK as a model. In this agreement, China promised that, under its "one country, two systems" formula, China's political and economic system would not be imposed on Macau, and that Macau would enjoy a "high degree of autonomy" in all matters except foreign affairs and defense for the next 50 years. However, after China's multi-year crackdown against the pro-democracy movement in nearby Hong Kong, the governments of China and the Macau Special Administrative Region worked to limit Macau's political autonomy by suppressing opposition activity in the 2021 legislative elections.
In April 1987, Portugal and China reached an agreement to return Macau to Chinese rule in 1999, using the Hong Kong Joint Declaration between China and the UK as a model. In this agreement, China promised that, under its "one country, two systems" formula, China's political and economic system would not be imposed on Macau, and that Macau would enjoy a "high degree of autonomy" in all matters except foreign affairs and defense for the next 50 years. However, after China's multi-year crackdown against the pro-democracy movement in nearby Hong Kong, the governments of China and the Macau Special Administrative Region worked to limit Macau's political autonomy by suppressing opposition activity in the 2021 legislative elections.
