
Italy
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Rome |
| Languages: | Italian (official), German (parts of Trentino-Alto Adige region are predominantly German-speaking), French (small French-speaking minority in Valle d'Aosta region), Slovene (Slovene-speaking minority in the Trieste-Gorizia area), Croatian (in Molise) |
People & Society
Ethnicity
Religion (2020 est.)
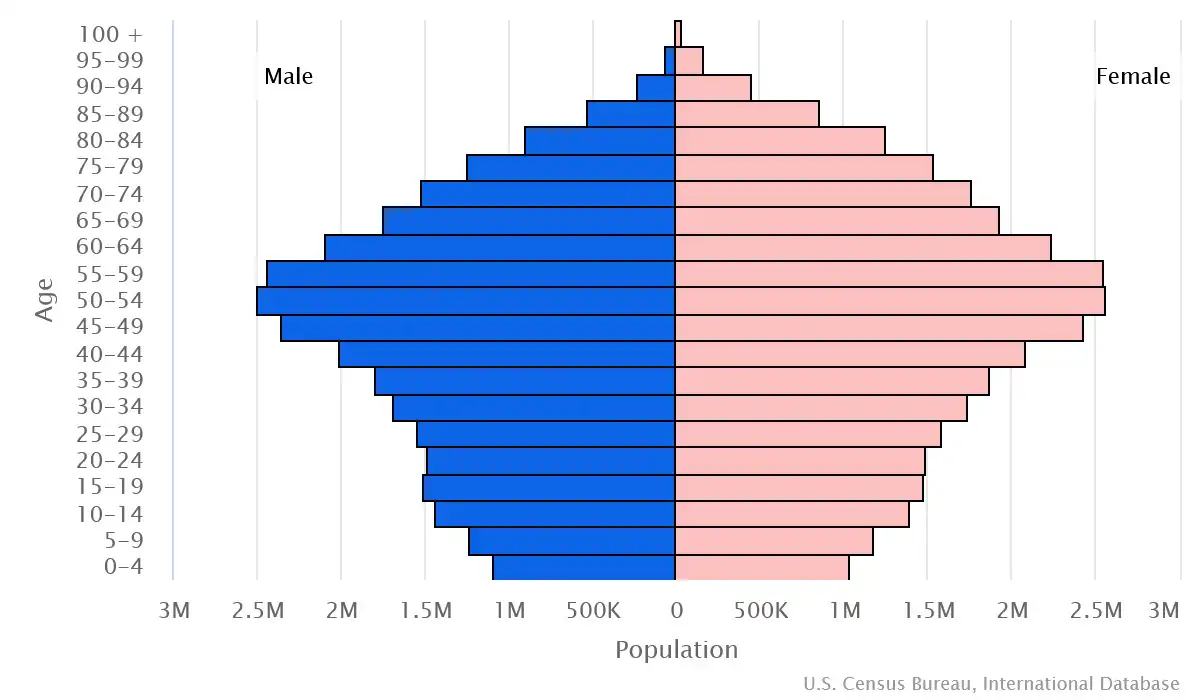
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
core EU economy; strong services, manufacturing, and tourism sectors; sustained recovery in post-COVID inflationary environment; high public debt levels; increasing poverty levels particularly in poorer south; strong exports to EU and US partners
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (40%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- natural gas 💨
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- cars 🚗
- packaged medicine 💊
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (40%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- packaged medicine 💊
- refined petroleum ⛽
- garments 👕
- cars 🚗
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
Geography
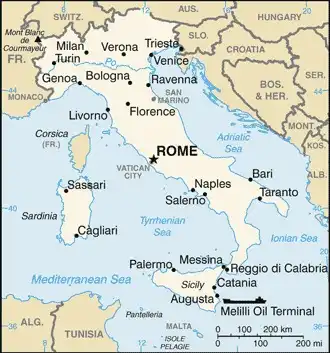
Map
Area
Natural resources
- coal ⚫
- antimony 🏺
- mercury ⚗️
- zinc 🔩
- potash 🪙
- marble 🪨
- barite 🪨
- asbestos 🏭💨
- pumice 🪨
- fluorspar 💎
- feldspar 🪨
- pyrite (sulfur) 🧪
- natural gas and crude oil reserves 🛢️
- fish 🐟
- arable land 🌱
Climate
predominantly Mediterranean; alpine in far north; hot, dry in south
Historical Background Information
Italy became a nation-state in 1861 when the regional states of the peninsula, along with Sardinia and Sicily, were united under King Victor EMMANUEL II. An era of parliamentary government came to a close in the early 1920s when Benito MUSSOLINI established a Fascist dictatorship. His alliance with Nazi Germany led to Italy's defeat in World War II. A democratic republic replaced the monarchy in 1946, and economic revival followed. Italy is a charter member of NATO, as well as the European Economic Community (EEC) and its successors, the EC and the EU. It has been at the forefront of European economic and political unification, joining the Economic and Monetary Union in 1999. Persistent problems include sluggish economic growth, high youth and female unemployment, organized crime, corruption, and economic disparities between southern Italy and the more prosperous north.
