
Iraq
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | federal parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Baghdad |
| Languages: | Arabic (official), Kurdish (official); Turkmen (a Turkish dialect) and Syriac (Neo-Aramaic) are recognized as official languages where native speakers of these languages are present |
People & Society
Ethnicity
Religion (2015 est.)
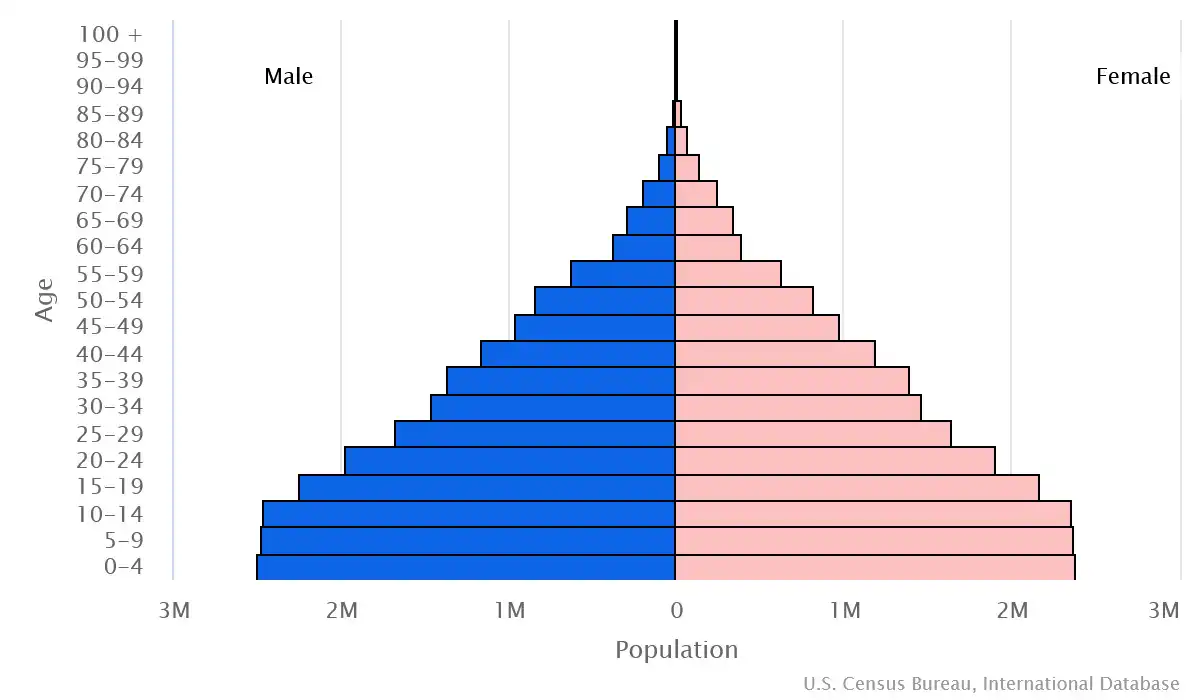
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
highly oil-dependent Middle Eastern economy; fiscal sustainability subject to fluctuation in oil prices; rising public confidence in economic conditions; import-dependent for most sectors; persistent challenges of corruption, informal markets, banking access, and political fragility
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (79%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- cars 🚗
- jewelry 💍
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (79%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- refined petroleum ⛽
- gold 💰
- petroleum coke 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
Geography
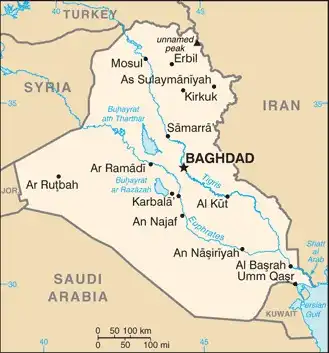
Map
Area
Natural resources
- petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- phosphates ⛏️
- sulfur 🧪
Climate
mostly desert; mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers; northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding in central and southern Iraq
Historical Background Information
Formerly part of the Ottoman Empire, Iraq was occupied by the United Kingdom during World War I and was declared a League of Nations mandate under UK administration in 1920. Iraq attained its independence as a kingdom in 1932. It was proclaimed a republic in 1958 after a coup overthrew the monarchy, but in actuality, a series of strongmen ruled the country until 2003. The last was SADDAM Hussein, from 1979 to 2003. Territorial disputes with Iran led to an inconclusive and costly war from 1980 to 1988. In 1990, Iraq seized Kuwait but was expelled by US-led UN coalition forces during the two-month-long Gulf War of 1991. After Iraq's expulsion, the UN Security Council (UNSC) required Iraq to scrap all weapons of mass destruction and long-range missiles and to allow UN verification inspections. Continued Iraqi noncompliance with UNSC resolutions led to the Second Gulf War in 2003, when US-led forces ousted the SADDAM regime.
In 2005, Iraqis approved a constitution in a national referendum and elected a 275-member Council of Representatives (COR). The COR approved most of the cabinet ministers, marking the transition to Iraq's first constitutional government in nearly a half-century. Iraq's constitution also established the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG), a semi-autonomous region that administers the governorates of Erbil, Dahuk, and As Sulaymaniyah. Iraq has held four national legislative elections since 2006, most recently in 2021. The COR approved Mohammad Shia' al-SUDANI as prime minister in 2022. Iraq has repeatedly postponed elections for provincial councils -- last held in 2013 -- and since 2019, the prime minister has had the authority to appoint governors rather than provincial councils.
Between 2014 and 2017, Iraq fought a military campaign against the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS) to recapture territory the group seized in 2014. In 2017, then-Prime Minister Haydar al-ABADI publicly declared victory against ISIS, although military operations against the group continue in rural areas. Also in 2017, Baghdad forcefully seized disputed territories across central and northern Iraq from the KRG, after a non-binding Kurdish independence referendum.
