
Iceland
Veröffentlicht: 19. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
364,036
Growth: 0.85% (2024 est.)
GDP
$31.325 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
103,000 sq km
| Government type: | unitary parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Reykjavik |
| Languages: | Icelandic, English, Polish, Nordic languages, German |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2024 est.)
Religion (2024 est.)
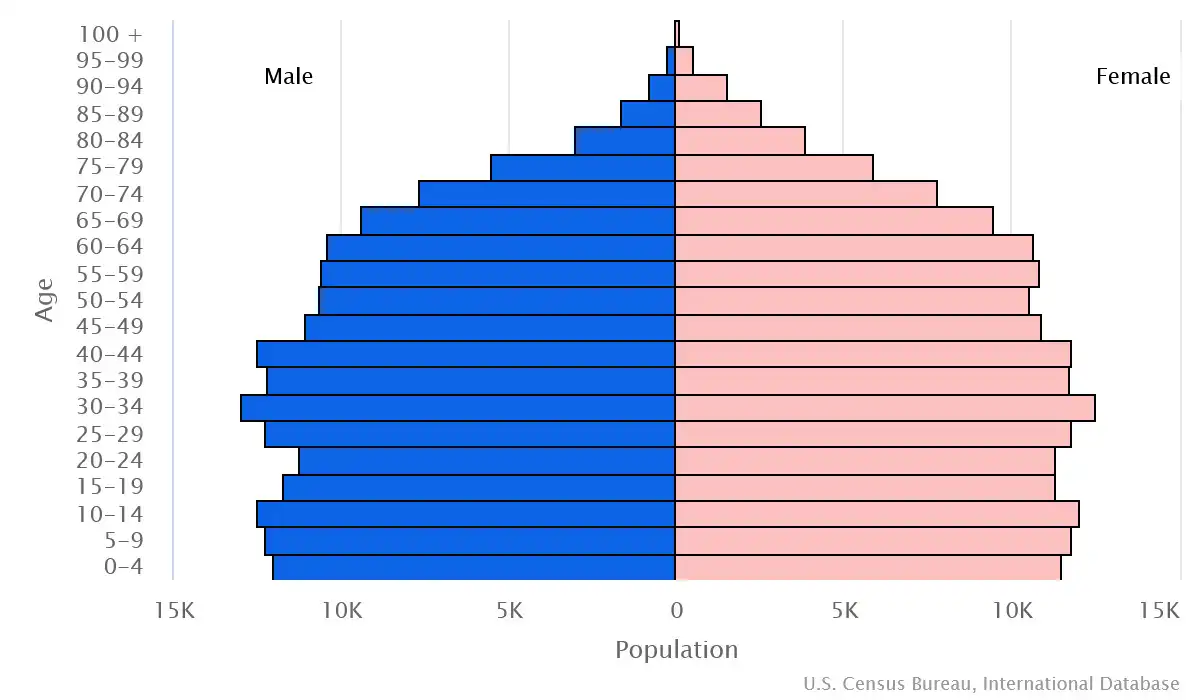
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income north Atlantic island economy; non-EU member but market integration via European Economic Area (EEA); dominant tourism, fishing, and aluminum industries vulnerable to demand swings and volcanic activity; inflation remains above target rate; barriers to foreign business access and economic diversification
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (45%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- aluminum oxide 🪙
- cars 🚗
- carbon-based electronics 💻
- aircraft ✈️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (45%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- fish 🐟
- aluminum 🪙
- iron alloys 🪓
- aluminum wire 🪙
- animal meal 🍖
Geography
Map
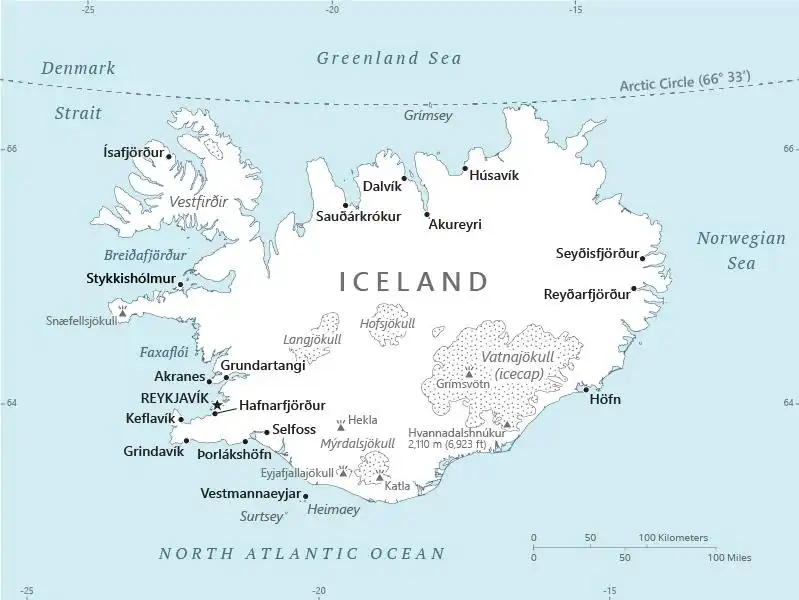
Area
Natural resources
- fish 🐟
- hydropower 💧⚡
- geothermal power 🌋
- diatomite 🪨
Climate
temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
Historical Background Information
Settled by Norwegian and Celtic (Scottish and Irish) immigrants during the late 9th and 10th centuries A.D., Iceland boasts the world's oldest functioning legislative assembly, the Althingi, which was established in 930. Independent for over 300 years, Iceland was subsequently ruled by Norway and Denmark. Fallout from the Askja volcano of 1875 devastated the Icelandic economy and caused widespread famine. Over the next quarter-century, 20% of the island's population emigrated, mostly to Canada and the US. Denmark granted limited home rule in 1874 and complete independence in 1944. The second half of the 20th century saw substantial economic growth driven primarily by the fishing industry. The economy diversified greatly after the country joined the European Economic Area in 1994, but the global financial crisis hit Iceland especially hard in the years after 2008. The economy is now on an upward trajectory, primarily thanks to a tourism and construction boom. Literacy, longevity, and social cohesion are first-rate by world standards.
