
Guinea
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Conakry |
| Languages: | French (official), Pular, Maninka, Susu, other native languages |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2018 est.)
Religion (2018 est.)
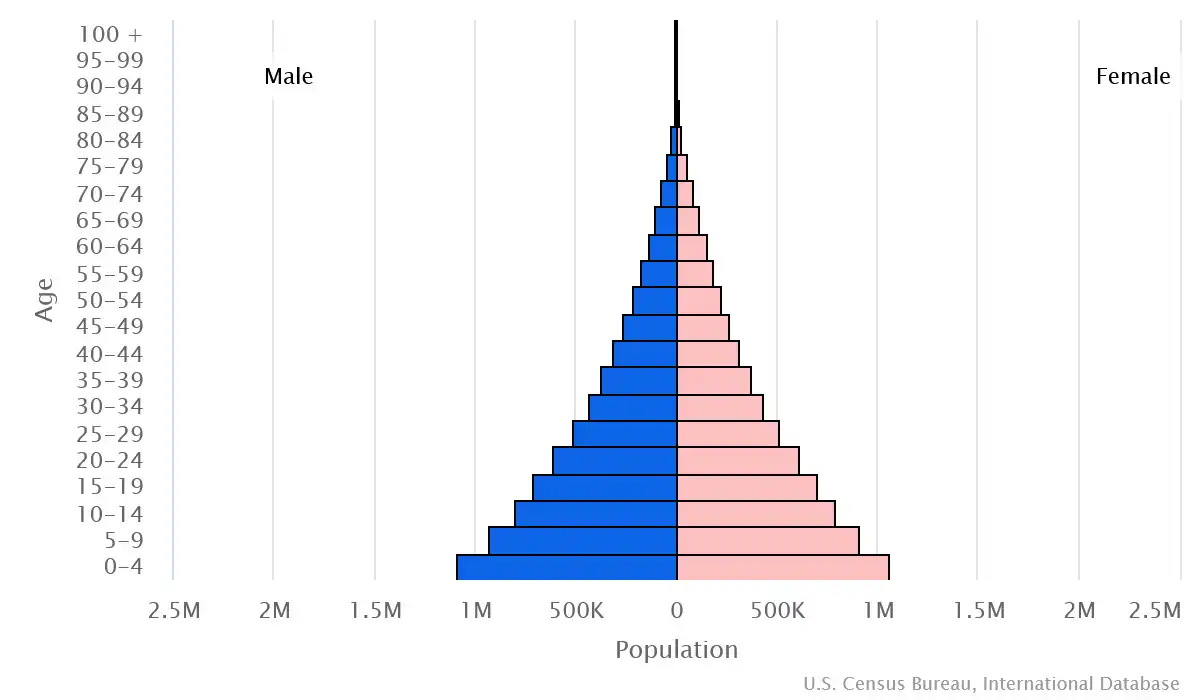
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
growing but primarily agrarian West African economy; major mining sector; improving fiscal and debt balances prior to COVID-19; economy increasingly vulnerable to climate change; slow infrastructure improvements; gender wealth and human capital gaps
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (63%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- rice 🍚
- garments 👕
- plastic products ♻️
- wheat 🌾
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (63%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- gold 💰
- aluminum ore 🪙
- coconuts/Brazil nuts/cashews 🌰
- cocoa beans 🍫
- fish 🐟
Geography
Map
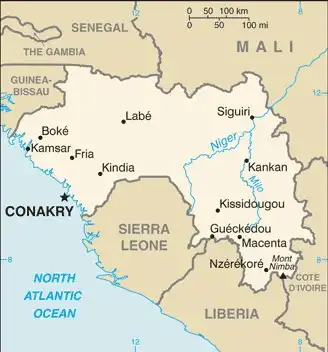
Area
Natural resources
- bauxite 🪨
- iron ore ⛓️
- diamonds 💎
- gold 💰
- uranium ☢️
- hydropower 💧⚡
- fish 🐟
- salt 🧂
Climate
generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds
Historical Background Information
Guinea's deep Muslim heritage arrived via the neighboring Almoravid Empire in the 11th century. Following Almoravid decline, Guinea existed on the fringe of several African kingdoms, all competing for regional dominance. In the 13th century, the Mali Empire took control of Guinea and encouraged its already growing Muslim faith. After the fall of the West African empires, various smaller kingdoms controlled Guinea. In the 18th century, Fulani Muslims established an Islamic state in central Guinea that provided one of the earliest examples of a written constitution and alternating leadership. European traders first arrived in the 16th century, and the French secured colonial rule in the 19th century.
In 1958, Guinea achieved independence from France. Sekou TOURE became Guinea’s first post-independence president; he established a dictatorial regime and ruled until his death in 1984, after which General Lansana CONTE staged a coup and seized the government. He too established an authoritarian regime and manipulated presidential elections until his death in 2008, when Captain Moussa Dadis CAMARA led a military coup, seized power, and suspended the constitution. In 2009, CAMARA was wounded in an assassination attempt and was exiled to Burkina Faso. In 2010 and 2013 respectively, the country held its first free and fair presidential and legislative elections. Alpha CONDE won the 2010 and 2015 presidential elections, and his first cabinet was the first all-civilian government in Guinean history. CONDE won a third term in 2020 after a constitutional change to term limits. In 2021, Col Mamady DOUMBOUYA led another successful military coup, establishing the National Committee for Reconciliation and Development (CNRD), suspending the constitution, and dissolving the government and the legislature. DOUMBOUYA was sworn in as transition president and appointed Mohamed BEAVOGUI as transition prime minister. The National Transition Council (CNT), which acts as the legislative body for the transition, was formed in 2022 and consists of appointed members representing a broad swath of Guinean society.
