
Finland
Veröffentlicht: 18. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
5,626,414
Growth: 0.2% (2024 est.)
GDP
$295.532 billion
(2023 est.)
Area
338,145 sq km
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Helsinki |
| Languages: | Finnish (official) 85.9%, Swedish (official) 5.2%, Russian 1.7%, other 7.2% (2022 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2022 est.)
Religion (2022 est.)
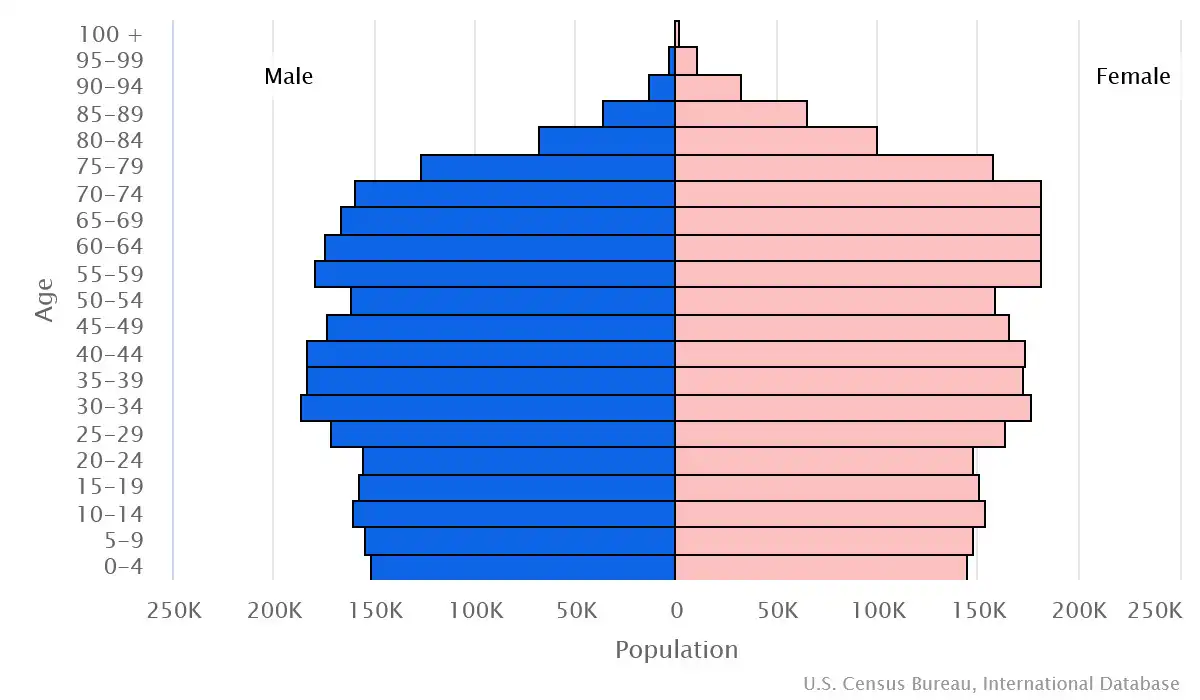
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
high-income, export-based EU and eurozone economy; major timber, metals, engineering, telecom, and electronics industries; emerging from recession triggered by inflation, weak consumer and export demand, and lower private investment; labor market reform plan to address structural rigidities
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (50%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
- electricity ⚡
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (50%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- paper 📄
- refined petroleum ⛽
- steel 🛠️
- wood pulp 🌲
- wood 🌲
Geography
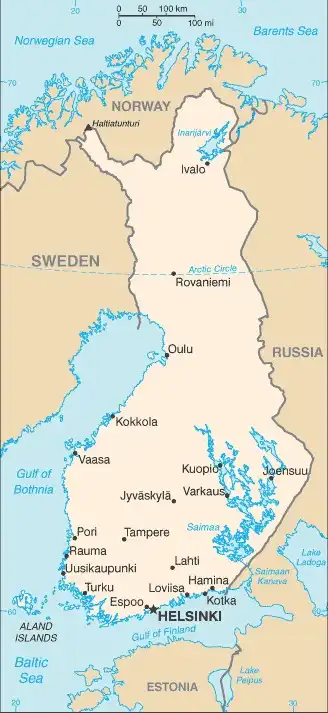
Map
Area
Natural resources
- timber 🌲
- iron ore ⛓️
- copper 🟧🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- chromite 🪨
- nickel 🪙
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
- limestone 🪨
Climate
cold temperate; potentially subarctic but comparatively mild because of moderating influence of the North Atlantic Current, Baltic Sea, and more than 60,000 lakes
Historical Background Information
Finland was a province and then a grand duchy under Sweden from the 12th to the 19th centuries and an autonomous grand duchy of Russia after 1809. It gained complete independence in 1917. During World War II, Finland successfully defended its independence through cooperation with Germany and resisted subsequent invasions by the Soviet Union, albeit with some loss of territory. During the next half-century, Finland transformed from a farm/forest economy to a diversified modern industrial economy; per-capita income is among the highest in Western Europe. A member of the EU since 1995, Finland was the only Nordic state to join the euro single currency at its initiation in January 1999. In the 21st century, the key features of Finland's modern welfare state are high-quality education, promotion of equality, and a national social welfare system, although the system is currently facing the challenges of an aging population and the fluctuations of an export-driven economy. Following Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Finland opted to join NATO; it became the organization's 31st member in April 2023.
