
Cuba
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | communist state |
| Capital: | Havana |
| Languages: | Spanish (official) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2012 est.)
Religion (2020 est.)
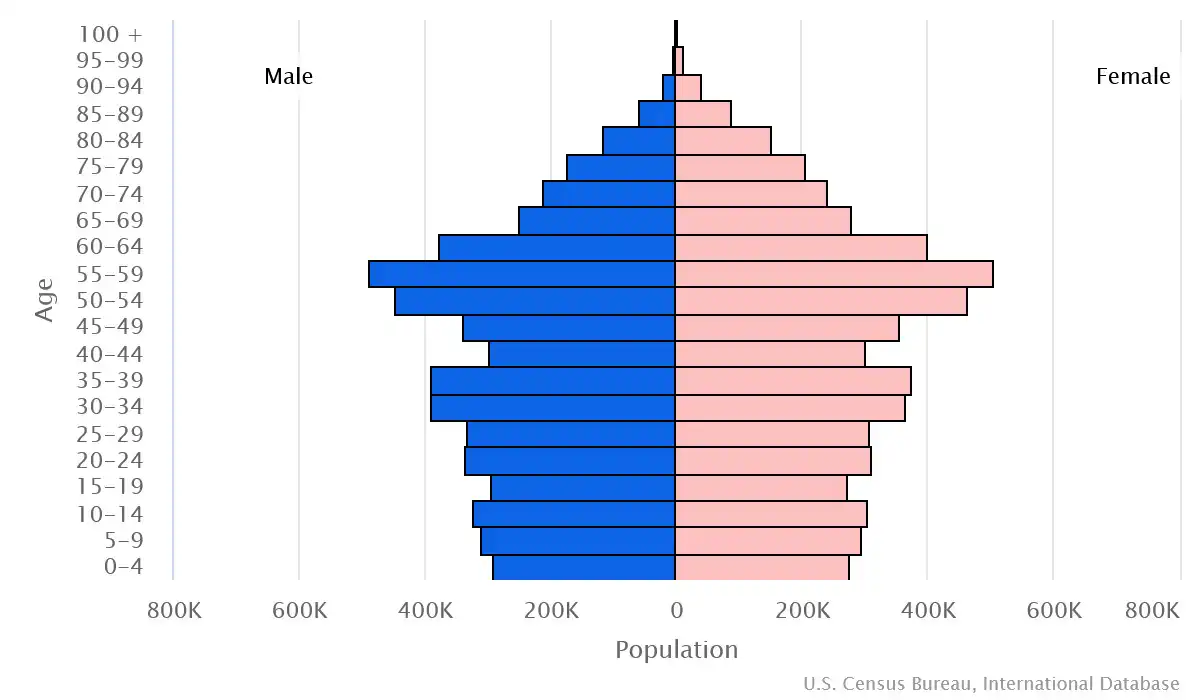
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
still largely state-run planned economy, although privatization increasing under new constitution; widespread protests due to lack of basic necessities and electricity; massive foreign investment increases recently; known tobacco exporter; unique oil-for-doctors relationship with Venezuela; widespread corruption
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (59%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- poultry 🍗
- wheat 🌾
- milk 🥛
- plastic products ♻️
- soybean oil 🛢️
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (59%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- tobacco 🚬
- nickel 🪙
- zinc ore 🔩
- liquor 🍷
- raw sugar 🍚
Geography
Map
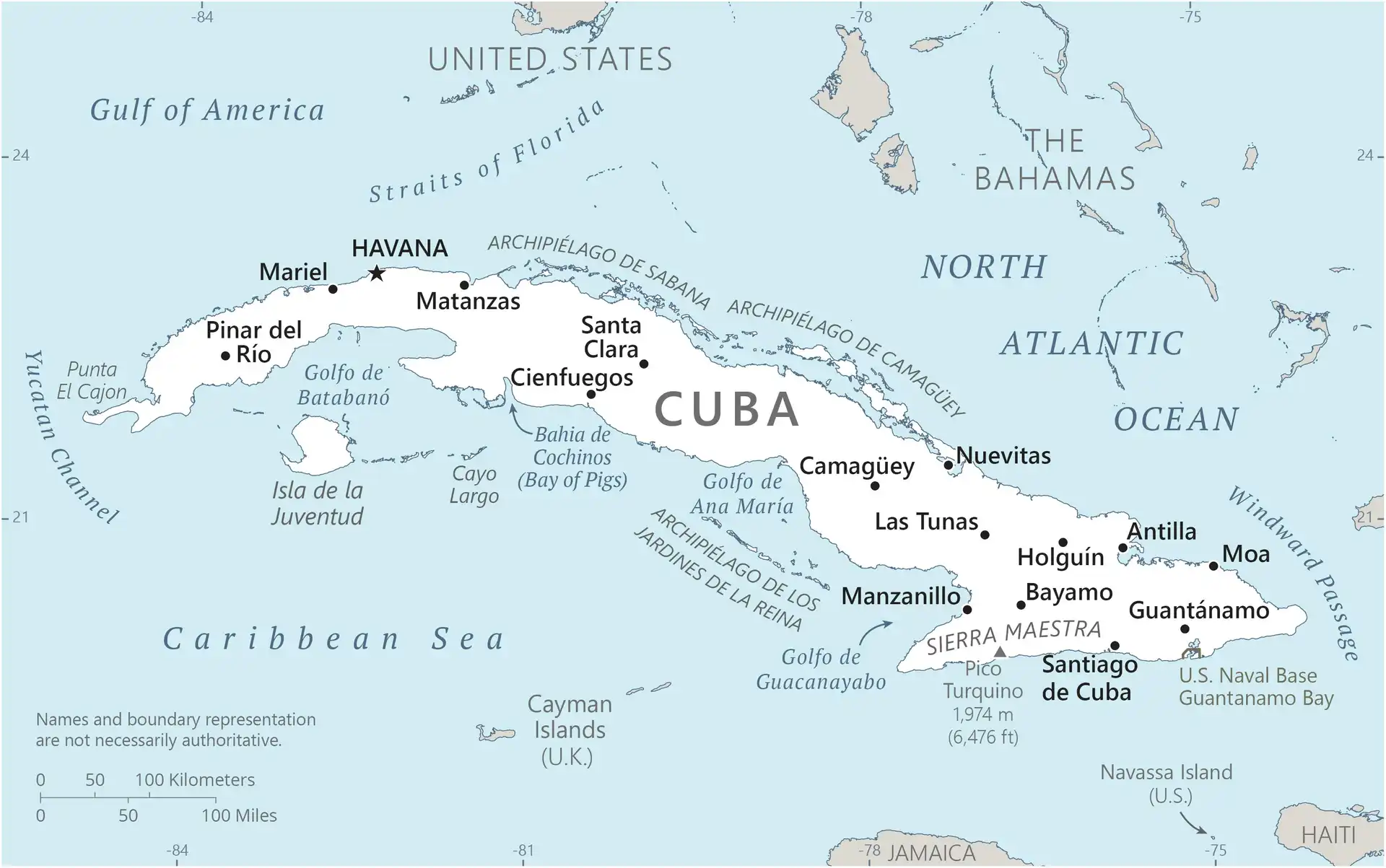
Area
Natural resources
- cobalt 🪙
- nickel 🪙
- iron ore ⛓️
- chromium 🟩
- copper 🟧🪙
- salt 🧂
- timber 🌲
- silica 🪨
- petroleum 🛢️
- arable land 🌱
Climate
tropical; moderated by trade winds; dry season (November to April); rainy season (May to October)
Historical Background Information
The native Amerindian population of Cuba began to decline after the arrival of Christopher COLUMBUS in 1492, as the country was developed as a Spanish colony during the next several centuries. Large numbers of African slaves were imported to work the coffee and sugar plantations, and Havana became the launching point for the annual treasure fleets bound for Spain from Mexico and Peru. Spanish rule eventually provoked an independence movement, and occasional rebellions were harshly suppressed. US intervention during the Spanish-American War in 1898 assisted the Cubans in overthrowing Spanish rule. The Treaty of Paris established Cuban independence from Spain in 1898, and after three-and-a-half years of subsequent US military rule, Cuba became an independent republic in 1902.
Cuba then experienced a string of governments mostly dominated by the military and corrupt politicians. Fidel CASTRO led a rebel army to victory in 1959; his authoritarian rule held the subsequent regime together for nearly five decades. He handed off the presidency to his younger brother Raul CASTRO in 2008. Cuba's communist revolution, with Soviet support, was exported throughout Latin America and Africa during the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez, hand-picked by Raul CASTRO to succeed him, was approved as president by the National Assembly and took office in 2018. DIAZ-CANEL was appointed First Secretary of the Communist Party in 2021 after the retirement of Raul CASTRO and continues to serve as both president and first secretary.
Cuba traditionally and consistently portrays the US embargo, in place since 1961, as the source of its socioeconomic difficulties. As a result of efforts begun in 2014 to reestablish diplomatic relations, the US and Cuba reopened embassies in their respective countries in 2015. The embargo remains in place, however, and the relationship between the US and Cuba remains tense. Illicit migration of Cuban nationals to the US via maritime and overland routes has been a longstanding challenge. In 2017, the US and Cuba signed a Joint Statement ending the so-called "wet-foot, dry-foot" policy, by which Cuban nationals who reached US soil were permitted to stay. Irregular Cuban maritime migration has dropped significantly since 2016, when migrant interdictions at sea topped 5,000, but land border crossings continue.
