
Christmas Island
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | non-self-governing overseas territory of Australia |
| Capital: | The Settlement (Flying Fish Cove) |
| Languages: | English (official) 27.6%, Mandarin 17.2%, Malay 17.1%, Cantonese 3.9%, Min Nan 1.6%, Tagalog 1%, other 4.5%, unspecified 27.1% (2016 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2001)
Religion (2016 est.)
Age structure
No image available.
Economy
Economic overview
high-income Australian territorial economy; development through government services and phosphate mining; operates Australia’s Immigration Detention Centre; increasing tourism and government investments; sustained environmental protections
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
no data
Real GDP per capita in $
No data
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (99%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- iron structures 🛠️
- air conditioners
- paintings 🪙
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (99%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- phosphates ⛏️
- fertilizers 💩
- chemical analysis instruments 🪨
- electrical transformers
- measuring instruments 🍹
Geography
Map
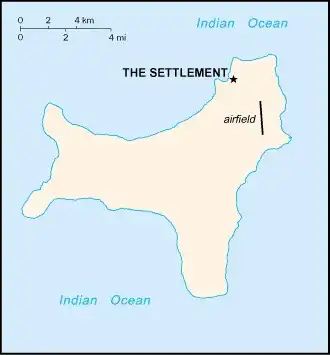
Area
Natural resources
- phosphate 🧪
- beaches
Climate
tropical with a wet season (December to April) and dry season; heat and humidity moderated by trade winds
Historical Background Information
Although Europeans sighted Christmas Island in 1615, it was named for the day of its rediscovery in 1643. Steep cliffs and dense jungle hampered attempts to explore the island over the next two centuries. The discovery of phosphate on the island in 1887 led to the UK annexing it the following year. In 1898, 200 Chinese indentured servants were brought in to work the mines, along with Malays, Sikhs, and a small number of Europeans. The UK administered Christmas Island from Singapore.
Japan invaded the island in 1942, but islanders sabotaged Japanese mining operations, making the mines relatively unproductive. After World War II, Australia and New Zealand bought the company mining the phosphate, and in 1958, the UK transferred sovereignty from Singapore to Australia in exchange for $20 million to compensate for the loss of future phosphate income. In 1980, Australia set up the Christmas Island National Park and expanded its boundaries throughout the 1980s until it covered more than 60% of the island’s territory. The phosphate mine was closed in 1987 because of environmental concerns, and Australia has rejected several efforts to reopen it.
In the 1980s, boats of asylum seekers started landing on Christmas Island, and the migrants claimed refugee status because they were on Australian territory. In 2001, Australia declared Christmas Island to be outside the Australian migration zone and built an immigration detention center on the island. Completed in 2008, the controversial detention center was closed in 2018 but then reopened in 2019. In 2020, the center served as a coronavirus quarantine facility for Australian citizens evacuated from China.
