
Brazil
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | federal presidential republic |
| Capital: | Brasília |
| Languages: | Portuguese (official and most widely spoken language); less common languages include Spanish (border areas and schools), German, Italian, Japanese, English, and many minor Amerindian languages |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2022 est.)
Religion (2023 est.)
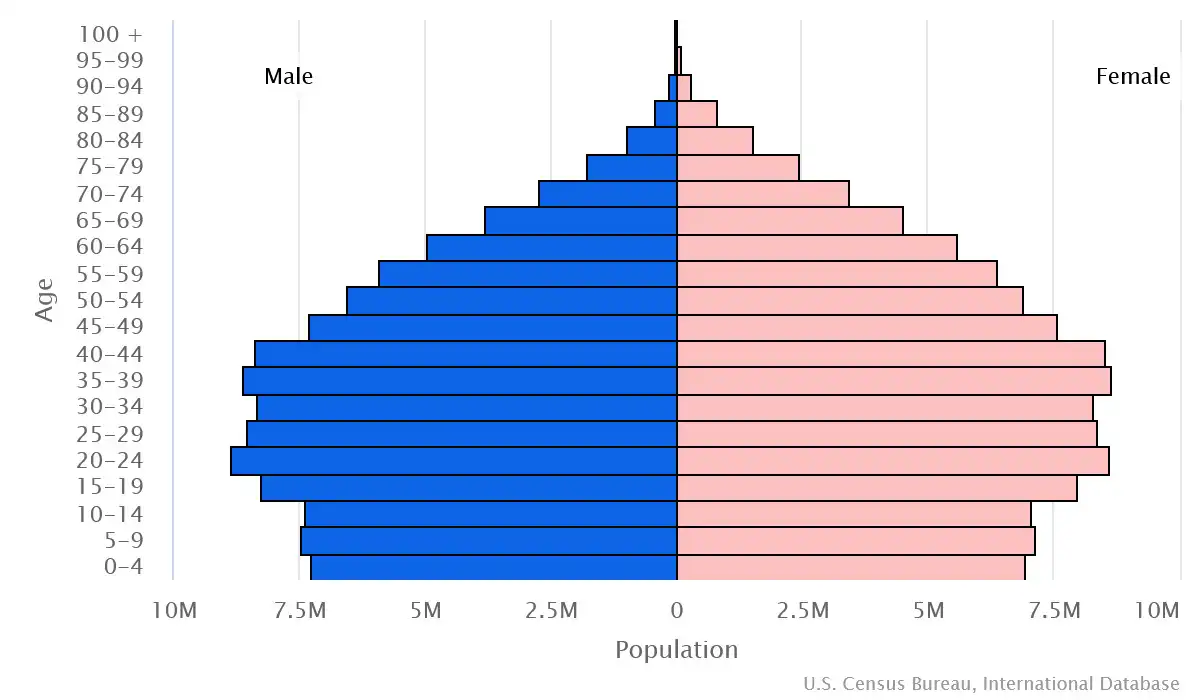
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
upper-middle income, largest Latin American economy; Mercosur, BRICS, G20 member and OECD accession candidate; growth driven by strong domestic consumption; tax simplification reforms aimed at addressing business conditions and lagging productivity; high inequality in income and access to health and education
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (56%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fertilizers 💩
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- pesticides 💉🌿
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (56%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- soybeans 🫘
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- iron ore ⛓️
- refined petroleum ⛽
- corn 🌽
Geography
Map
Area
Natural resources
- alumina 🪶
- bauxite 🪨
- beryllium 🟩
- gold 💰
- iron ore ⛓️
- manganese 🪙
- nickel 🪙
- niobium 🟦
- phosphates ⛏️
- platinum 🪙
- tantalum 🪙
- tin 🪙
- rare earth elements 🪨🪙💎
- uranium ☢️
- petroleum 🛢️
- hydropower 💧⚡
- timber 🌲
Climate
mostly tropical, but temperate in south
Historical Background Information
After more than three centuries under Portuguese rule, Brazil gained its independence in 1822, maintaining a monarchical system of government until the abolition of slavery in 1888 and the subsequent proclamation of a republic by the military in 1889. Brazilian coffee exporters politically dominated the country until populist leader Getúlio VARGAS rose to power in 1930. VARGAS governed through various versions of democratic and authoritarian regimes from 1930 to 1945. Democratic rule returned in 1945 -- including a democratically elected VARGAS administration from 1951 to 1954 -- and lasted until 1964, when the military overthrew President João GOULART. The military regime censored journalists and repressed and tortured dissidents in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The dictatorship lasted until 1985, when the military regime peacefully ceded power to civilian rulers, and the Brazilian Congress passed its current constitution in 1988.
By far the largest and most populous country in South America, Brazil continues to pursue industrial and agricultural growth and development of its interior. Having successfully weathered a period of global financial difficulty in the late 20th century, Brazil was soon seen as one of the world's strongest emerging markets and a contributor to global growth under President Luiz Inácio LULA da Silva (2003-2010). The awarding of the 2014 FIFA World Cup and 2016 Summer Olympic Games -- the first ever to be held in South America -- to Brazil was symbolic of the country's rise. However, from about 2013 to 2016, Brazil was plagued by a sagging economy, high unemployment, and high inflation, only emerging from recession in 2017. Congress removed then-President Dilma ROUSSEFF (2011-2016) from office in 2016 for having committed impeachable acts against Brazil's budgetary laws, and her vice president, Michel TEMER, served the remainder of her second term. A money-laundering investigation, Operation Lava Jato, uncovered a vast corruption scheme and prosecutors charged several high-profile Brazilian politicians with crimes. Former President LULA was convicted of accepting bribes and served jail time (2018-19), although his conviction was overturned in 2021. LULA's revival became complete in 2022 when he narrowly defeated incumbent Jair BOLSONARO (2019-2022) in the presidential election. Positioning Brazil as an independent global leader on climate change and promoting sustainable development, LULA took on the 2024 G20 presidency, balancing the fight against deforestation with sustainable energy and other projects designed to alleviate poverty and promote economic growth, such as expanding fossil fuel exploration.
