
Bouvet Island
Veröffentlicht: 18. June 2022 - Letztes Update: 28. February 2025
Country Data Dashboard
Population
uninhabited
Growth: -
GDP
no data
Area
49 sq km
| Government type: | - |
| Capital: | - |
| Languages: | - |
Economy
Economic overview
-Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
no data
Real GDP per capita in $
No data
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (96%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- aluminum structures 🪙
- animal products 🥩
- cement 🏗️
- air pumps 💨
- electrical transformers
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (96%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- fish 🐟
- tensile testing machines 🪙
- jewelry 💍
- paper 📄
- garments 👕
Geography
Map
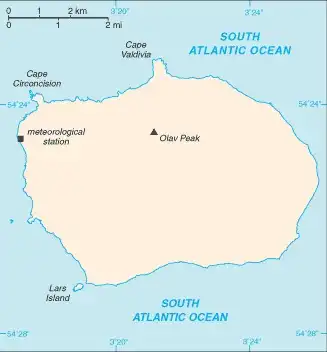
Area
Natural resources
- none 🚫
Climate
antarctic
Historical Background Information
This uninhabited volcanic island in Antarctica is almost entirely covered by glaciers, making it difficult to approach. Bouvet Island is recognized as the most remote island on Earth because it is furthest from any other point of land (1,639 km from Antarctica). The island was named after the French naval officer who discovered it in 1739, although no country laid claim to it until 1825, when the British flag was raised. A few expeditions visited the island in the late 19th century. In 1929, the UK waived its claim in favor of Norway, which had occupied the island two years previously. In 1971, Norway designated Bouvet Island and the adjacent territorial waters as a nature reserve. Since 1977, Norway has run an automated meteorological station and studied foraging strategies and distribution of fur seals and penguins on the island. In 2006, an earthquake weakened the station's foundation, causing it to be blown out to sea in a winter storm. Norway erected a new research station in 2014 that can hold six people for periods of two to four months.
