
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Sarajevo |
| Languages: | Bosnian (official) 52.9%, Serbian (official) 30.8%, Croatian (official) 14.6%, other 1.6%, no answer 0.2% (2013 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (2013 est.)
Religion (2013 est.)
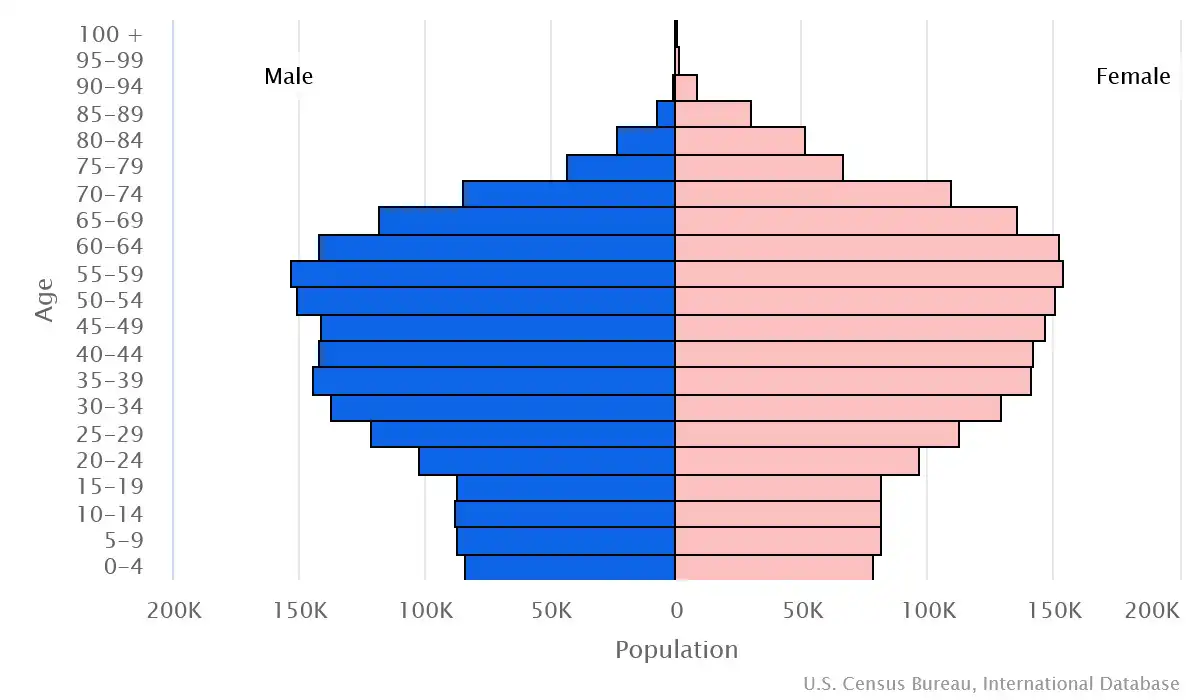
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
import-dominated economy; remains consumption-heavy; lack of private sector investments and diversification; jointly addressing structural economic challenges; Chinese energy infrastructure investments; high unemployment; tourism industry impacted by COVID-19
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (52%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- refined petroleum ⛽
- aluminum 🪙
- garments 👕
- coal ⚫
- cars 🚗
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (52%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- aluminum 🪙
- electricity ⚡
- footwear 👞
- garments 👕
- plastic products ♻️
Geography
Map
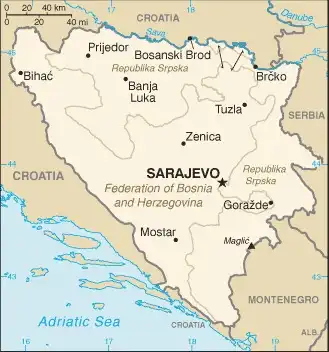
Area
Natural resources
- coal ⚫
- iron ore ⛓️
- antimony 🏺
- bauxite 🪨
- copper 🟧🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- chromite 🪨
- cobalt 🪙
- manganese 🪙
- nickel 🪙
- clay 🧱
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- salt 🧂
- sand 🏜️
- timber 🌲
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate
hot summers and cold winters; areas of high elevation have short, cool summers and long, severe winters; mild, rainy winters along coast
Historical Background Information
After four centuries of Ottoman rule over Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austria-Hungary took control in 1878 and held the region until 1918, when it was incorporated into the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. After World War II, Bosnia and Herzegovina joined the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY).
Bosnia and Herzegovina declared sovereignty in October 1991 and independence from the SFRY on 3 March 1992 after a referendum boycotted by ethnic Serbs. Bosnian Serb militias, with the support of Serbia and Croatia, then tried to take control of territories they claimed as their own. From 1992 to 1995, ethnic cleansing campaigns killed thousands and displaced more than two million people. On 21 November 1995, in Dayton, Ohio, the warring parties initialed a peace agreement, and the final agreement was signed in Paris on 14 December 1995.
The Dayton Accords retained Bosnia and Herzegovina's international boundaries and created a multiethnic and democratic government composed of two entities roughly equal in size: the predominantly Bosniak-Bosnian Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the predominantly Bosnian Serb-led Republika Srpska (RS). The Dayton Accords also established the Office of the High Representative to oversee the agreement's implementation. In 1996, the NATO-led Stabilization Force (SFOR) took over responsibility for enforcing the peace. In 2004, European Union peacekeeping troops (EUFOR) replaced SFOR. As of 2022, EUFOR deploys around 1,600 troops in Bosnia in a peacekeeping capacity. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an official candidate for EU membership in 2022.
