
Bhutan
Country Data Dashboard
| Government type: | constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Thimphu |
| Languages: | Sharchopkha 28%, Dzongkha (official) 24%, Lhotshamkha 22%, other 26% (includes foreign languages) (2005 est.) |
People & Society
Ethnicity (predominantly Lhotshampas)
Religion (2005 est.)
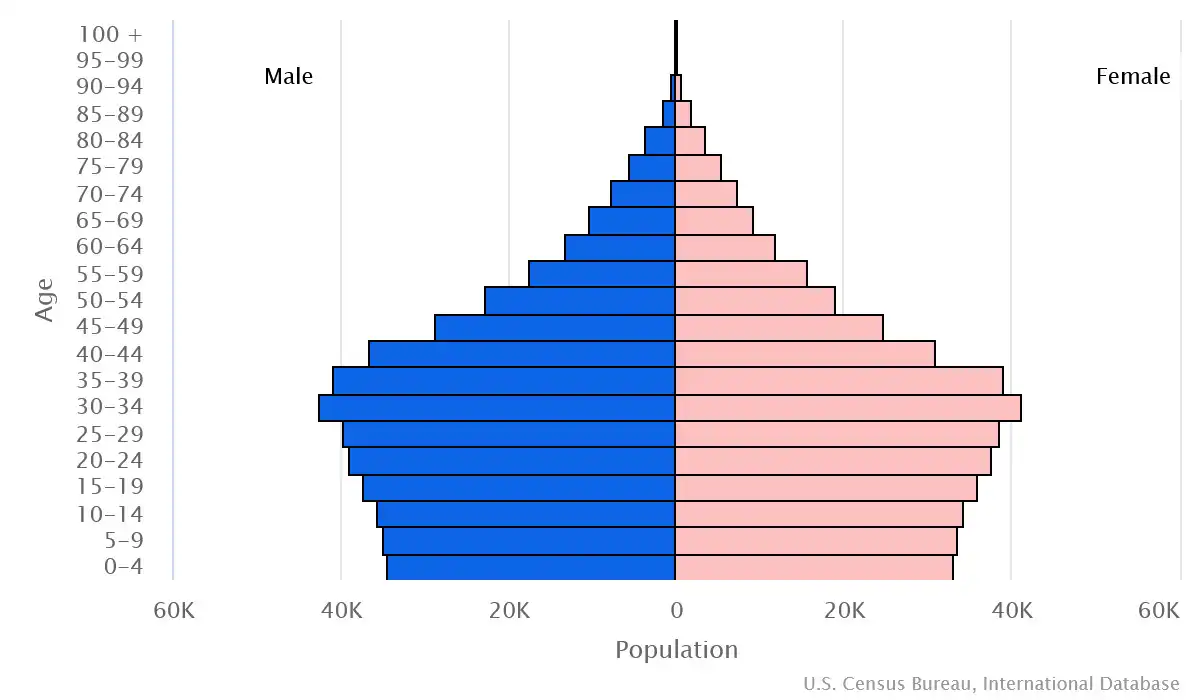
Age structure
Economy
Economic overview
hydropower investments spurring economic development; Gross National Happiness economy; sharp poverty declines; low inflation; strong monetary and fiscal policies; stable currency; fairly resilient response to COVID-19; key economic and strategic relations with India; climate vulnerabilities
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Real GDP per capita in $
Exports & Imports in million $
Top 5 Import Partner in 2022 (95%)
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022
- computers 💻
- refined petroleum ⛽
- electrical machinery ⚙️
- coke 🪨
- wood charcoal ⚫
Top 5 Export Partner in 2022 (95%)
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022
- iron alloys 🪓
- dolomite 🪨
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- cement 🏗️
- electricity ⚡
Geography
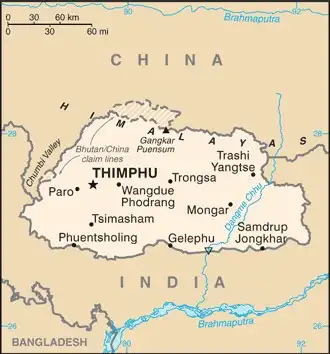
Map
Area
Natural resources
- timber 🌲
- hydropower 💧⚡
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- calcium carbonate 🪙
Climate
varies; tropical in southern plains; cool winters and hot summers in central valleys; severe winters and cool summers in Himalayas
Historical Background Information
After Britain’s victory in the 1865 Duar War, Britain and Bhutan signed the Treaty of Sinchulu, under which Bhutan would receive an annual subsidy in exchange for ceding land to British India. Ugyen WANGCHUCK -- who had served as the de facto ruler of an increasingly unified Bhutan and had improved relations with the British toward the end of the 19th century -- was named king in 1907. Three years later, a treaty was signed whereby the British agreed not to interfere in Bhutanese internal affairs, and Bhutan allowed Britain to direct its foreign affairs. Bhutan negotiated a similar arrangement with independent India in 1949. The Indo-Bhutanese Treaty of Friendship returned to Bhutan a small piece of the territory annexed by the British, formalized the annual subsidies the country received, and defined India's responsibilities in defense and foreign relations. Under a succession of modernizing monarchs beginning in the 1950s, Bhutan joined the UN in 1971 and slowly continued its engagement beyond its borders.
In 2005, King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK unveiled the draft of Bhutan's first constitution -- which introduced major democratic reforms -- and held a national referendum for its approval. The King abdicated the throne in 2006 in favor of his son, Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK. In 2007, India and Bhutan renegotiated their treaty, eliminating the clause that stated that Bhutan would be "guided by" India in conducting its foreign policy, although Thimphu continues to coordinate closely with New Delhi. In 2008, Bhutan held its first parliamentary election in accordance with the constitution. Bhutan experienced a peaceful turnover of power following a parliamentary election in 2013, which resulted in the defeat of the incumbent party. In 2018, the incumbent party again lost the parliamentary election. In 2024, of the more than 100,000 ethnic Nepali -- predominantly Lhotshampa -- refugees who fled or were forced out of Bhutan in the 1990s, about 6,500 remain displaced in Nepal.
